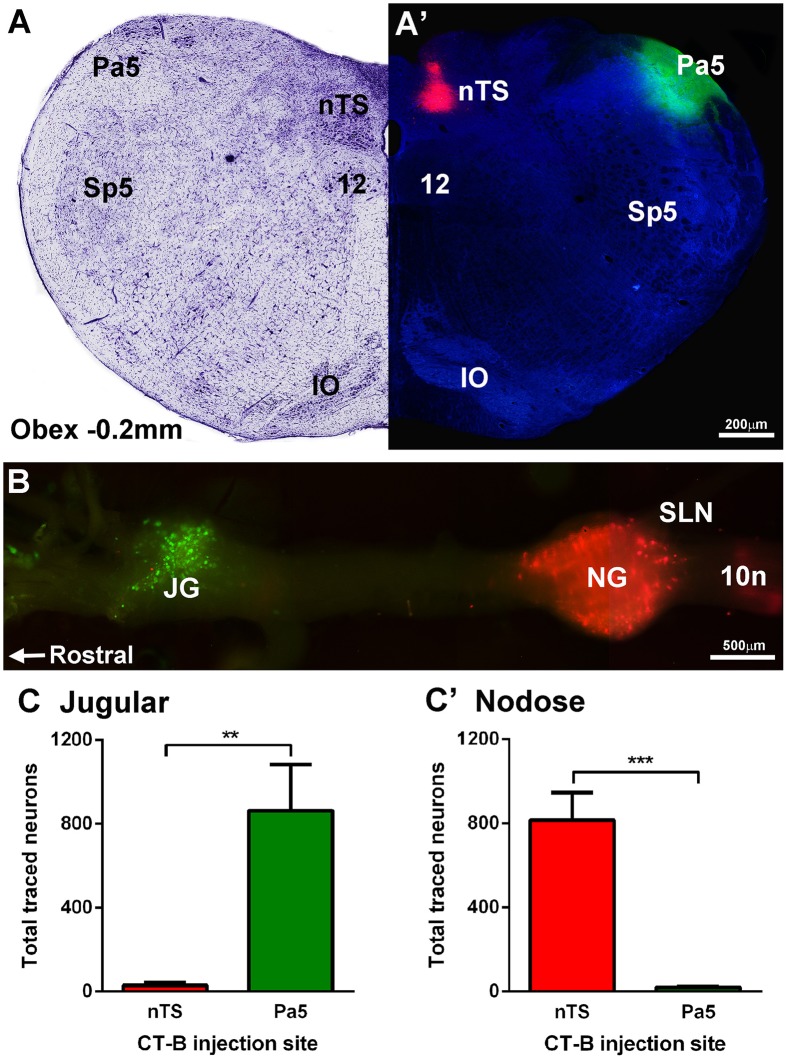
Figure 2.
Differential terminations of jugular and nodose vagal ganglia neurons in the paratrigeminal nucleus (Pa5) and nucleus of the solitary tract (nTS). (A,A′) Example photomicrograph and corresponding Nissl staining of a caudal brainstem section showing the Pa5 and nTS locations for microinjection of cholera toxin subunit-b (CT-B) tracers conjugated with 488 (green) or 594 (red) fluorophores, respectively. (B) Fluorescent photomicrograph of a wholemount preparation of the guinea pig vagal ganglia showing neuronal soma retrogradely labeled with CT-B from the Pa5 (green) and nTS (red). (C) Quantitative cell counts performed on serial ganglia sections, demonstrating that Pa5 projecting neurons reside in the jugular ganglia (JG) whereas (C′) nTS projecting neurons are located within the nodose ganglia (NG). Data represent the mean ± SEM number of neurons quantified from a minimum of 10 tissue sections of vagal ganglia obtained from n = 6 separate dual tracing experiments. **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001, significantly different pairwise comparison. Additional abbreviations: 10n, vagus nerve; 12, hypoglossal nucleus; IO, inferior olives; SLN, superior laryngeal nerve; Sp5, spinal trigeminal nucleus; sp5, spinal trigeminal tract.