Table 2.
Compounds that deplete mutant p53.
| Compound | Type of mutant | Mechanism | Reference | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hsp90 inhibitors: 17-AAG, geldanamycin, ganetespib | R175H, L194F, R248Q, R273H, R280K, R172H (mouse) | Reverse the Hsp90’s function to inactivate MDM2 and CHIP | (13, 66–69) | 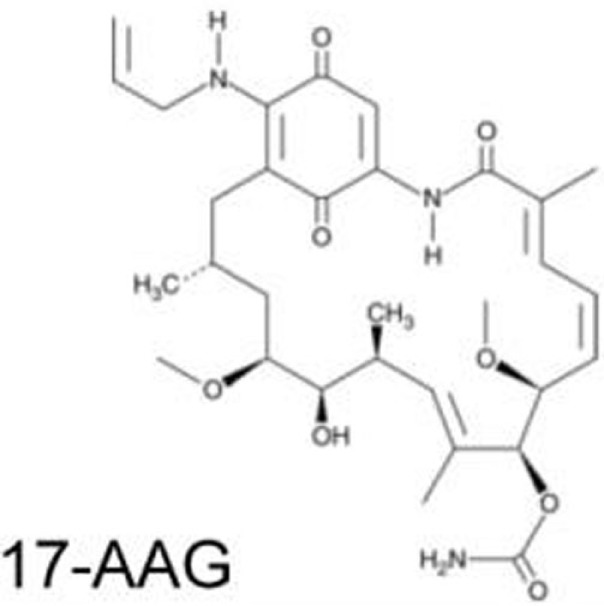 |
| HDAC inhibitors: vorinostat/SAHA, romidepsin/depsipeptide | R175H, R280K, V247F/P223L | Inhibit HDAC6 and disrupt the HDAC6/Hsp90/mutant p53 complex | (70–72) | 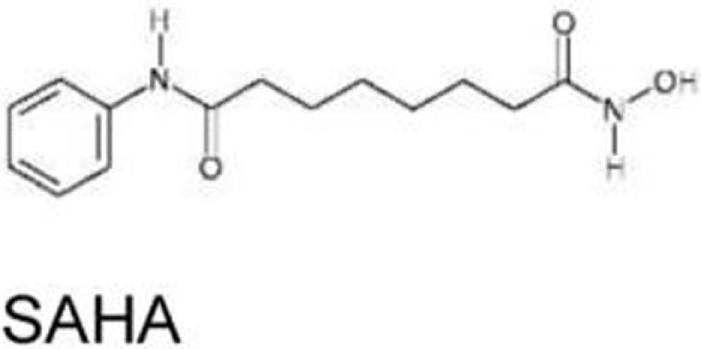 |
| Arsenic compounds | R175H, R248W, H179Y/R282W, R273H | Increase transcripts of Pirh2 and induce degradation of mutant p53 | (73, 74) | 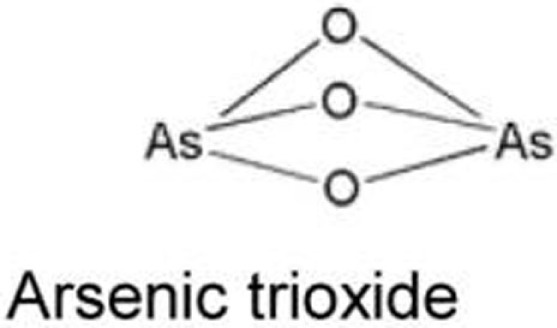 |
| Gambogic acid | R175H, G266E, R273H, R280K | Inhibit the mutant p53-Hsp90 complex and induce CHIP-dependent degradation | (75) | 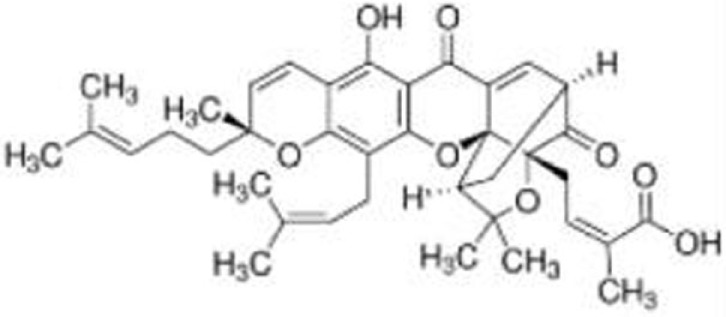 |
| Spautin-1 | R158lnF, R175H, S241F, R248Q, G266Q, R280L, R273H | Induce mutant p53 degradation via the CMA pathway activated by the suppression of macroautophagy under glucose-free and confluent conditions | (76, 77) | 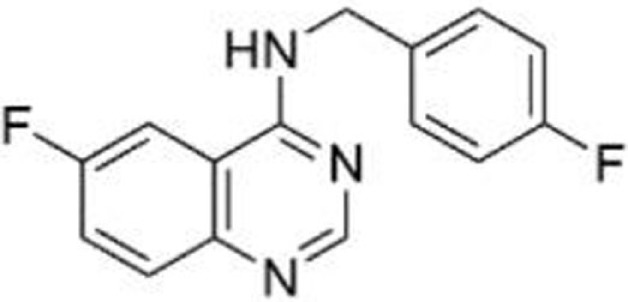 |
| YK-3-237 | V157F, M237I, R249S, R273H, R280K | Decrease mutant p53 levels through deacetylation at lysine 382 by activating SIRT1 | (78) | 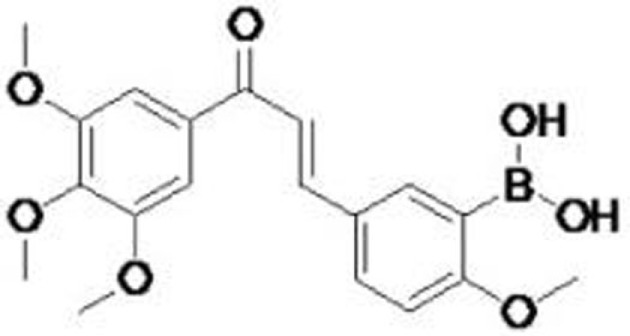 |
| NSC59984 | R175L, R175H, S241F, R273H/P309F | Induce MDM2-mediated mutant p53 degradation and activate p73 | (79) | 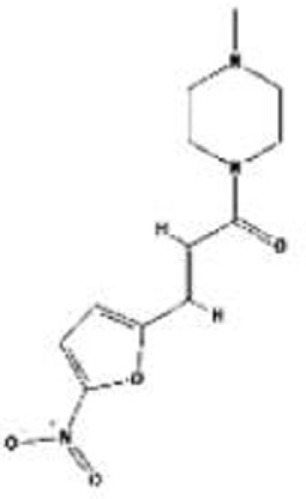 |
| Disulfiram (DSF) | R273H | Induce degradation of both wild-type p53 and p53R273H via the 26S proteasome pathway | (80) | 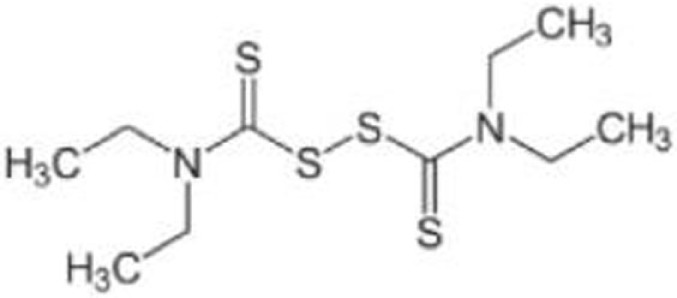 |
