Figure 2.
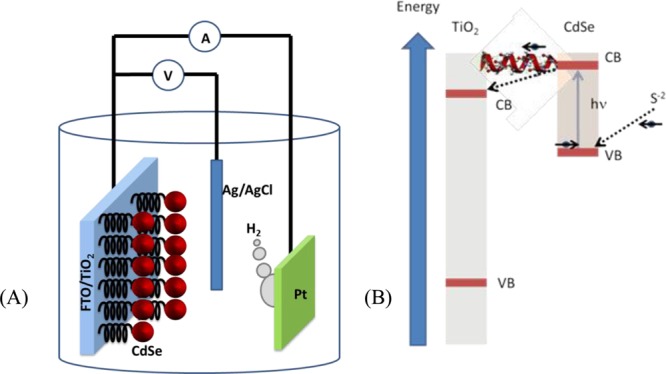
(A) Scheme of the photoelectrochemical cell used in the present study for water splitting. CdSe nanoparticles (red) are bound to the TiO2 nanoparticles through chiral molecules. The TiO2 nanoparticles are attached to the FTO conducting electrode. On the Pt electrode, the H+ ions are reduced to form H2. (B) Scheme of the electron transfer between the S2– and the TiO2 nanoparticles. Upon excitation of the CdSe nanoparticles, the excited electrons are transferred through the chiral molecules to TiO2 (from there to the external circuit). This is a spin-specific electron transfer because the transfer through the chiral molecule is preferred for one spin over the other. Thus, the hole in the CdSe has a well-defined spin alignment; therefore, electrons with this spin will be transferred from the anions in the solution to CdSe.
