Figure 6. An LPS variant dissociates CD14 and TLR4 endocytosis.
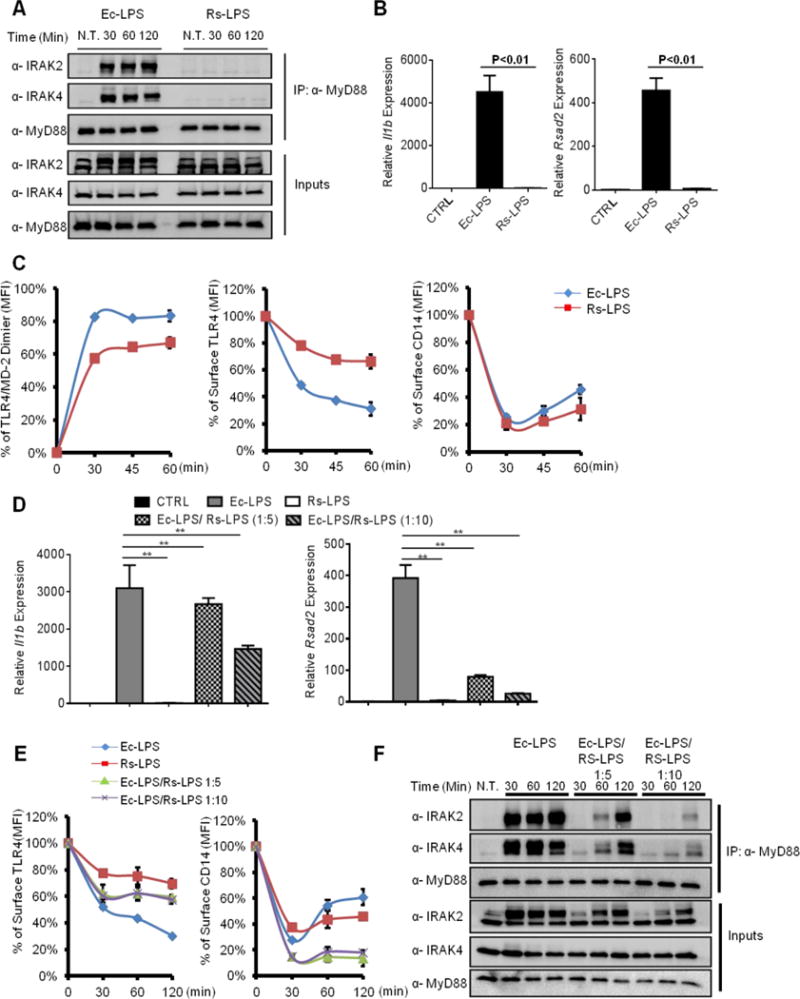
(A) iBMDMs were stimulated with E. coli LPS (Ec-LPS, 100 ng/ml) and R. sphaeroides LPS (Rs-LPS, 100 ng/ml) for indicated times. The assembly of myddosome was then examined by western blot.
(B) iBMDMs were treated with Ec-LPS (100 ng/ml) or Rs-LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 hours, il1b and rsad2 expression were measured by qPCR.
(C) iBMDMs were stimulated with LPS for times indicated. TLR4/MD-2 dimerization (left), TLR4 endocytosis (middle) and CD14 endocytosis (right) were determined by flow cytometry.
(D–F) iBMDMs were stimulated with Ec-LPS (100 ng/ml) and mixtures of Ec-LPS and Rs-LPS at the ratio of 1:5 or 1:10 (100 ng/ml Ec-LPS plus 500 ng/ml Rs-LPS or 100 ng/ml Ec-LPS plus 1000 ng/ml Rs-LPS) for 4 hours. il1b and rsad2 expression was then measured by qPCR.
(E, F) Similar treatments as D, except surface TLR4 (left) and CD14 (right) staining was determined by flow cytometry, or myddosome assembly was examined.
Error bars represent mean SEM from triplicate readings in one experiment. **,p<0.01.
