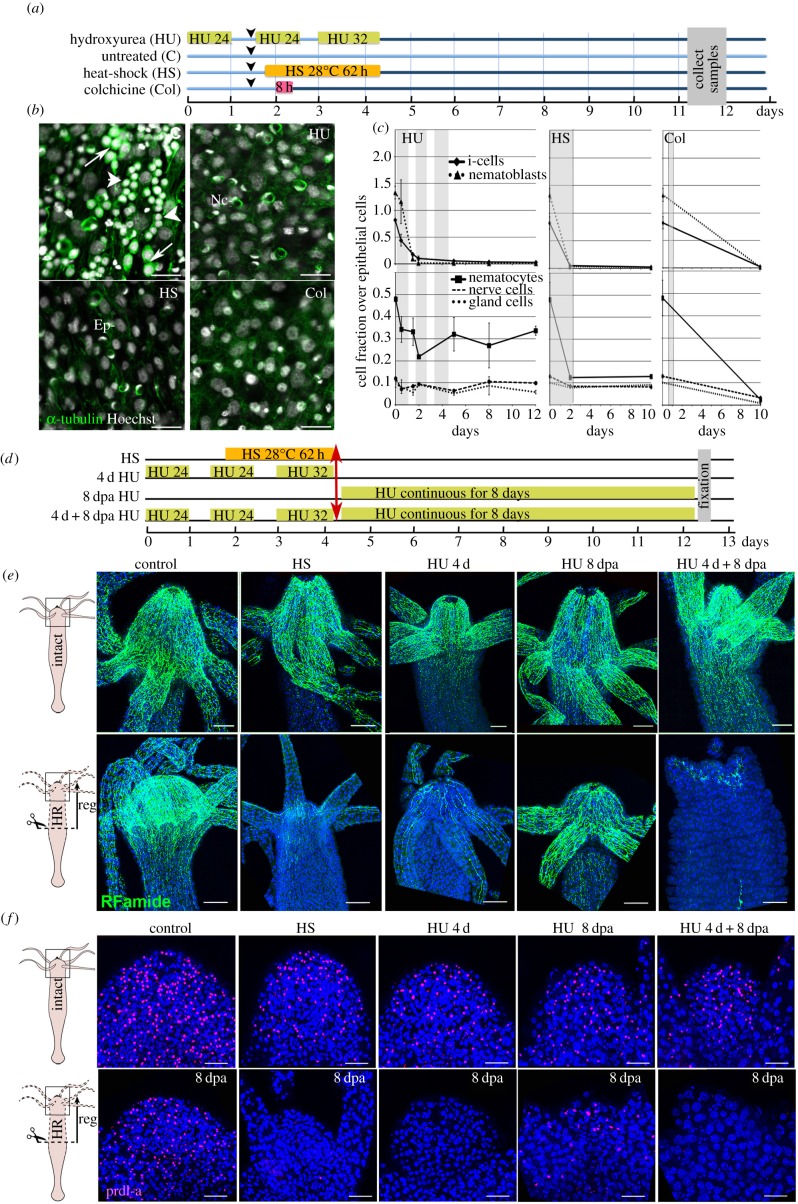
Figure 2.
Loss of apical neurogenesis in Hydra after HS, HU or Col treatment. (a) Scheme indicating the timeline for drug treatments (HU, Col) and HS exposure of animals. Arrowheads indicate feedings. (b) Ectodermal view of animals fixed at day 11 after HS, HU or Col exposure as indicated in (a) and immunostained for α-tubulin (green). Note the absence of interstitial cells (arrows) and nematoblasts (arrowheads) in treated samples. Ep, epithelial cells; Nc, nematocytes, white nuclei: Hoechst staining. Scale bar: 25 µm. (c) Quantification of i-cells, nematoblasts (upper panels), and i-cell derivatives (lower panels) over epithelial cells in animals exposed to HS, HU or Col. Tissues were macerated and stained as in (b). (d–f) Scheme depicting the regeneration experiments conducted on HS- or HU-treated animals (d). Animals bisected at mid-gastric position (red arrow) were left to regenerate either in HM (conditions HS, 4 d HU), or in HM containing HU (conditions 8 dpa HU, 4 d + 8 dpa HU), then fixed at 8 dpa and immunodetected with anti-RFamide (e) and anti-prdl-a (f) antibodies. (e) Anatomy of the apical nervous system detected with the anti-RFamide (green) antibody in intact (upper panels) and in head-regenerating (lower panels) animals. Scale bar: 100 µm. (f) Neuronal progenitors and apical neurons detected with anti-prdl-a immunostaining (red) in intact (upper panels) and regenerating heads (lower panels). Scale bar: 50 µm. Note the absence of neuronal progenitors after HS, 4 d HU and 4 d + 8 dpa HU and their reduced number in the 8 dpa HU condition. Blue: DAPI staining (e,f). dpa, days post-amputation.