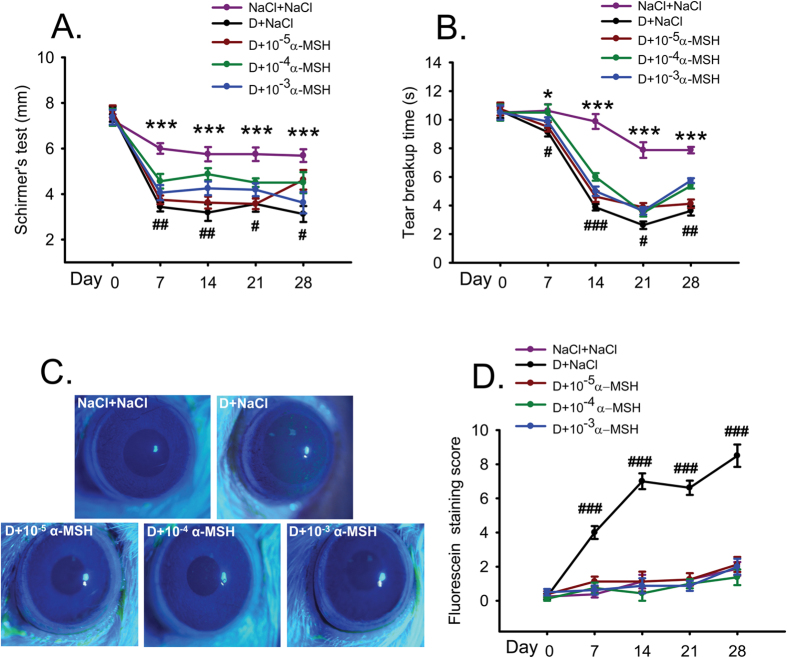
Figure 1. α-MSH at different doses ameliorated the ocular surface dysfunctions in the scopolamine-induced dry eye rats during the experimental time course.
The animals were divided into NaCl + NaCl (purple line), D + NaCl (black line), D + 10−5 α-MSH (dark red line), D + 10−4 α-MSH (green line), and D + 10−3 α-MSH (blue line) groups. The Schirmer’s test (A), tear breakup time (B), and corneal fluorescein staining (C,D) were examined weekly. Representative pictures of corneal fluorescein staining were shown (C). The staining scores were compared (D). n = 8 per group. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. D = dry eye, NaCl = saline.