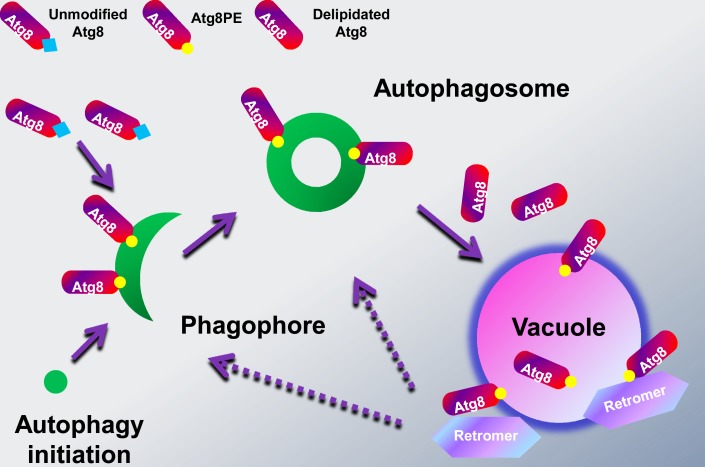
Fig 9. A model for the retromer function in Atg8 retrieval.
Autophagy requires the formation of double-membrane bound autophagosomes that associate with a set of evolutionarily conserved autophagy-related proteins, including Atg8. During the autophagocytosis, Atg8 has to be conjugated to the lipid phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), resulting in the expansion of the phagophore membrane and formation of autophgosomes. At the late stage, the autophagosomes fuse with the vacuoles to form autophagolysosomes to deliver the sequestered material for degradation and/or recycling. In yeast, the outer membrane-bound Atg8 was released into the cytosol by delipidation before autophagomes-vacuole fusion, presumably for reuse in subsequent rounds of autophagosome formation. In our study, we found that M. oryzae retromer core complex (MoVps35-MoVps26-MoVps29) localized at the late endosome/ prevacuolar membranes, where it interacts with cleaved and lipidated Atg8 thus regulating its trafficking to the phagophore or autophagosome and preventing its degradation in the lumen of vacuole.