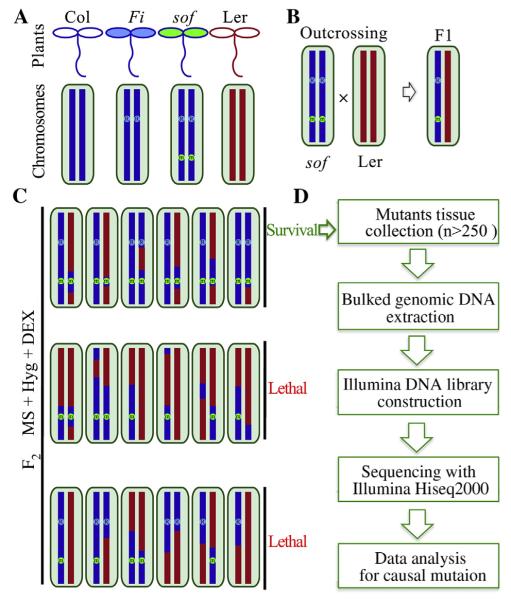
Fig. 4. NGS-mapping workflow.
A: The genome of Ler is in red and Col is in blue. From genetic analysis, we know that FREE1-RNAi transgenic plants harbor a single-insertion that we marked as R in blue. All sof mutants are assumed to harbor a mutation (m in green) caused by EMS. B: The putative mutant was first crossed to the Ler wild type. F1 hybrids inbreeded and gave rise to a segregating F2 mapping population. C: The causal mutation was identified using segregating populations from F2 via outcrossing with Ler ecotype wild type. Survived seedlings from F2 Seeds were pooled together for genomic DNA on medium containing both hygromycin antibiotics and DEX. In the case of recessive sof mutations, this will include only homozygous mutants, which should be around 3/16 of all seeds. D: Illumina sequencing library was constructed using obtained bulked DNA. Whole genome sequencing was performed using Hiseq2000 platform. Further sequencing data analysis would uncover the causal mutation.