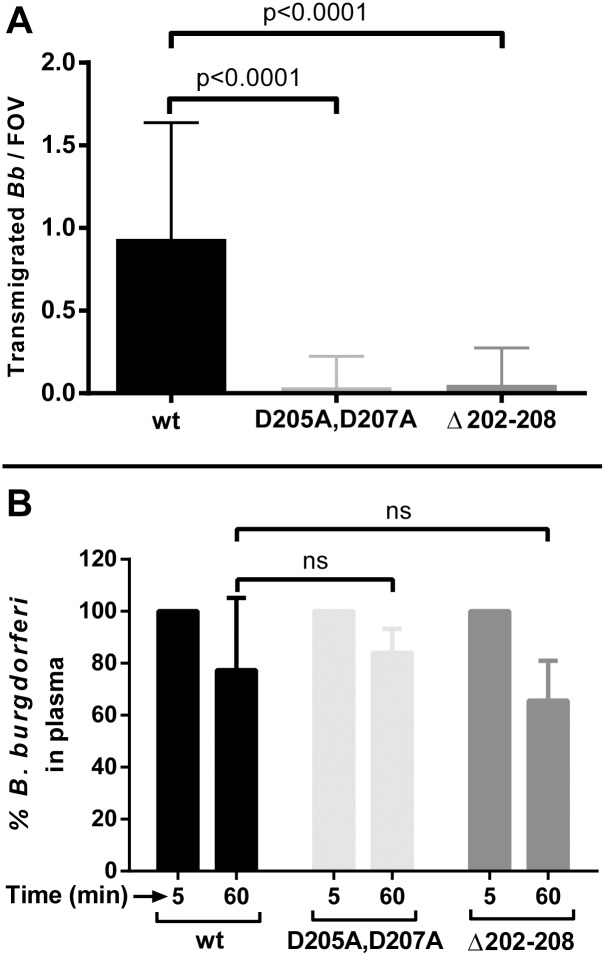
Fig 6. The effect of p66 site-directed integrin binding mutants on vascular transmigration and clearance in Cd1d -/- mice.
A) GFP-expressing B. burgdorferi strains, infectious wild type (GCB847), p66 D205A,D207A (GCB3003) and p66 Δ202–208 (GCB3004) were injected into the tail vein of Cd1d -/- mice (n = 3/group, 4x108 spirochetes were injected per mouse). After 24 hours, vascular transmigration was scored in the knee joint-proximal tissue in the living mice by intravital microscopy using a spinning disk laser confocal microscope. Blood vessels were stained with PE-conjugated PECAM-1 antibody and green fluorescent spirochetes outside of the vasculature were counted in at least five fields of view (FOV) per mouse. Statistical significance was analyzed using non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. P-values for select pairwise comparisons are shown; ns denotes not significant (P-values >0.05). B). Concentrations of B. burgdorferi in mouse plasma after iv inoculation. Cd1d -/- mice were injected with B. burgdorferi through the tail vein and blood was withdrawn at 5 and 60 minutes post-inoculation (n = 3/group). Blood cells were allowed to settle overnight as described in Materials and Methods and spirochetes in the plasma were directly counted by dark-field microscopy. The change in spirochete concentration between 5 and 60 minutes was determined for each mouse as the percentage of spirochetes present at 60 minutes relative to the initial 5 minute time point. Statistical significance was analyzed using non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. P-values for select pairwise comparisons are shown; ns denotes not significant (P-values >0.05).