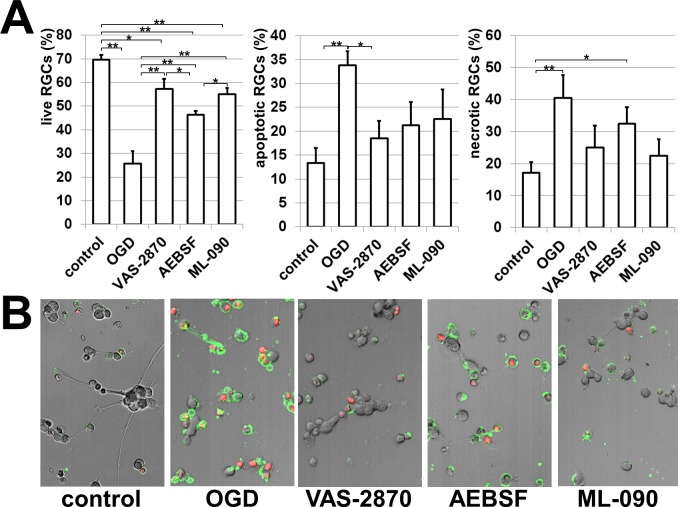
Figure 4.
NAD(P)H oxidases contribute to RGC death: (A) The NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors VAS-2870 (0.5 μM), AEBSF (0.5 μM), and ML-090 (0.09 μM) reduced OGD-induced RGC death. RGCs were deprived of oxygen and glucose for 4 hours followed by 24 hours of reoxygenation in either the presence or the absence of the NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors. The percentage of live RGCs as well as necrotic and apoptotic cells relative to the total number of cells was determined (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (B) Necrotic and apoptotic cells were identified using Annexin V (green) as a marker of apoptotic cells and Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI, red) to recognize necrotic cells.