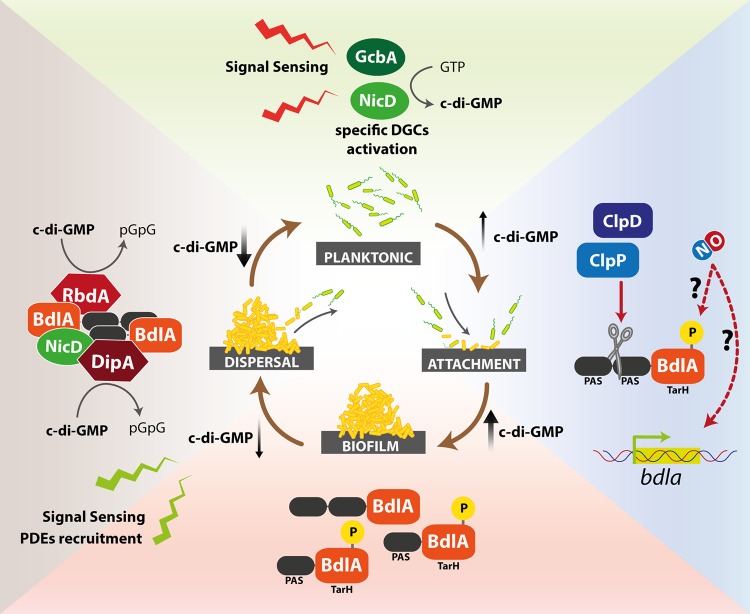
FIG 2.
Nitric oxide activation of the BdlA signaling cascade. The BdlA protein is a key player in the modulation of biofilm formation and dispersal. It may be activated by nutrient and/or other signals (NO); the complex events occurring during and after BdlA activation are summarized in this figure (clockwise). Signal sensing initially leads to a transient increase in c-di-GMP, possibly triggered by specific DGCs, such as NicD or GcbA. Activation of BdlA by site-specific proteolysis by ClpD/ClpP at the level of the PAS domains or by phosphorylation leads to a further increase in c-di-GMP levels and biofilm formation. Other signaling events may trigger the recruitment of c-di-GMP-specific PDEs (RbdA and DipA), ultimately leading to a decrease in c-di-GMP levels and biofilm dispersal.