Figure 5.
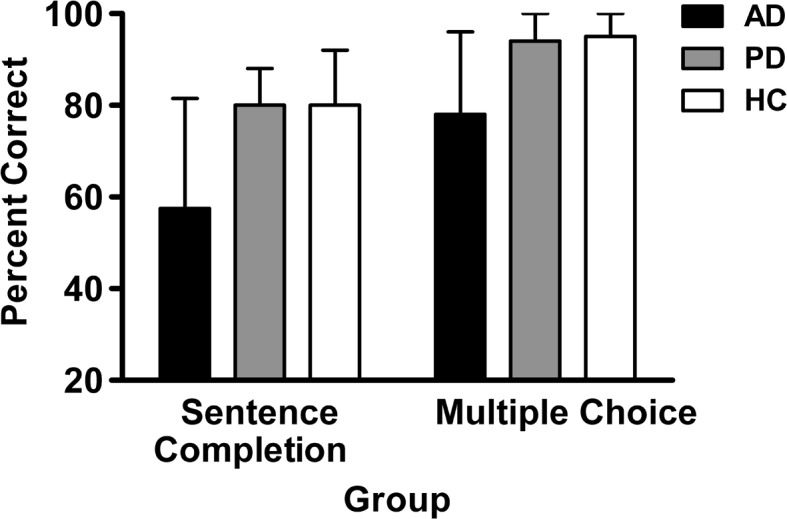
Results from the Northridge Evaluation of Formulas, Idioms and Proverbs in Social Situations for sentence completion and multiple-choice tasks for three participant groups: healthy controls (HC), speakers with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and speakers with Parkinson's disease (PD). Significant differences were found for sentence completion—AD versus HC, t(26) = 3.448, p = .002; AD versus PD, t(24) = 3.572, p = .002—and for multiple-choice tasks—AD versus HC, t(24) = 3.779, p = .002; AD versus PD, t(21) = 3.138, p = .005.
