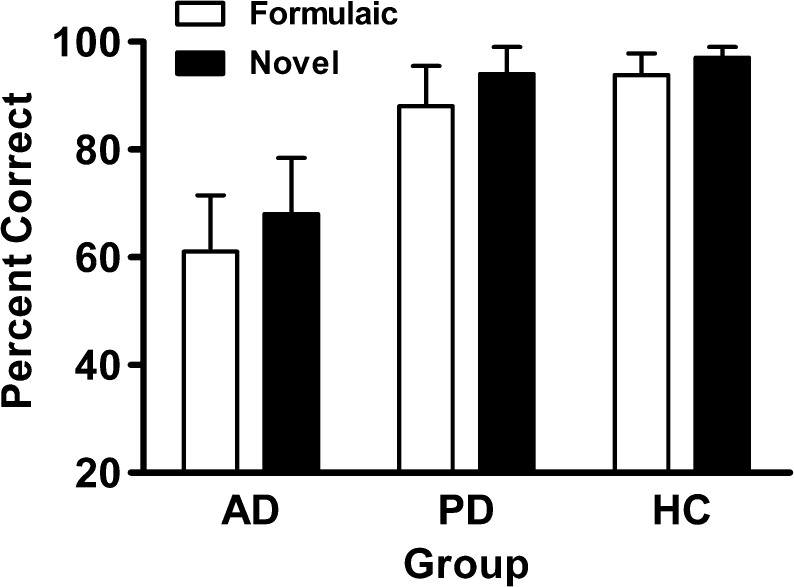
Figure 6.
Formulaic and Novel Language Comprehension performance on novel and formulaic expressions in three participant groups: healthy controls (HC), speakers with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and speakers with Parkinson's disease (PD). HC versus AD on formulaic subtest, t(28) = 5.491, p < .001; HC versus AD on novel subtest, t(27) = 4.357, p < .001; PD versus AD on formulaic subtest, t(26) = 4.176, p < .001; PD versus AD on novel subtest, t(26) = 3.423, p = .002.