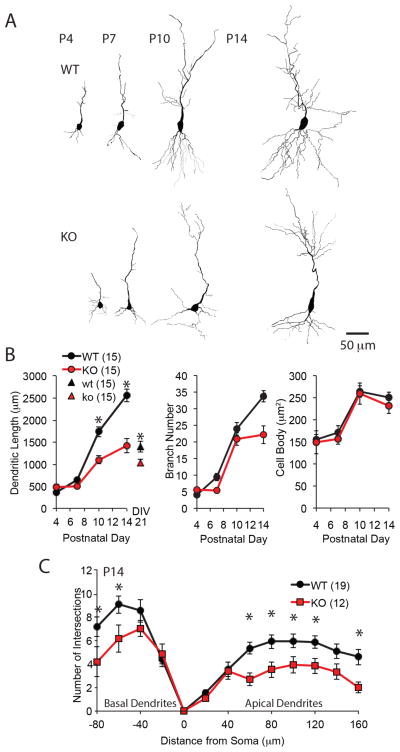
Figure 2. Constrained dendritic morphology of CA1 pyramidal neurons in MMP-9−/− mice.
(A) Reconstruction of representative Golgi stained CA1 pyramidal neurons from WT (top) and MMP-9−/− (KO; bottom) mice at P4, P7, P10 and P14. (B) Quantification of total dendritic length, number of branches and size of cell bodies over development (n=15 neurons from 4 subjects each condition, One-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(2,29)=53.8; p<0.0001, 17.4; p<0.0001, and 1.05; p=0.314, respectively, *p<0.05, WT vs. KO, Tukey-Kramer post hoc test). Quantification of total dendritic length in vitro (n=15, neurons from 5 cultures for each group, *p=0.017, Student’s T-test) shown for comparison triangles in B left. (C) Sholl analysis of number intersections of proximal dendrites. Distance from soma is plotted positively and negatively for apical and basal dendrites, respectively (n=19 neurons from 4 subjects for WT, 12 neurons from 4 subjects for KO. One-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(2,30)=11.3; p=0.002 and 4.58; p=0.041, respectively, *p<0.05, WT vs. KO, Tukey-Kramer post hoc test).