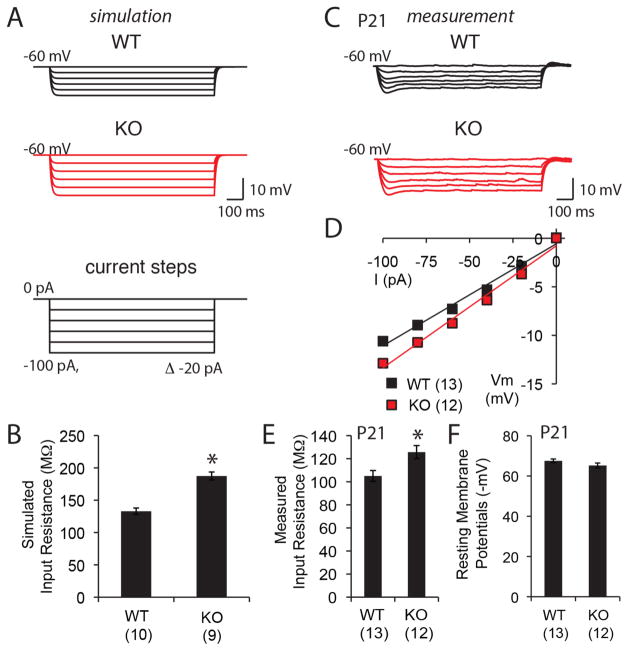
Figure 3. Higher input resistance in CA1 pyramidal neurons of MMP-9−/− mice.
(A) Simulated steady-state voltage responses of WT and MMP-9−/− (KO) CA1 pyramidal neurons. Current injections (1000 ms somatic step) ranged from 0 pA to −100 pA in −20 pA increments. (B) Simulated values of input resistance (n=10 neurons from 4 subjects for WT, 9 neurons from 4 subjects for KO). (C) Real voltage responses of WT and KO CA1 pyramidal neurons. Injection of somatic step currents for 1000 ms ranging from 0 pA to −100 pA in −20 pA increments. (D) Current-voltage curve for WT and KO measured in real CA1 neurons. (E) and (F) Measurements of input resistance at −60 mV, and resting membrane potentials (n=13 neurons from 4 subjects for WT, 12 neurons from 4 subjects for KO). *p<0.05; Student’s T-test.