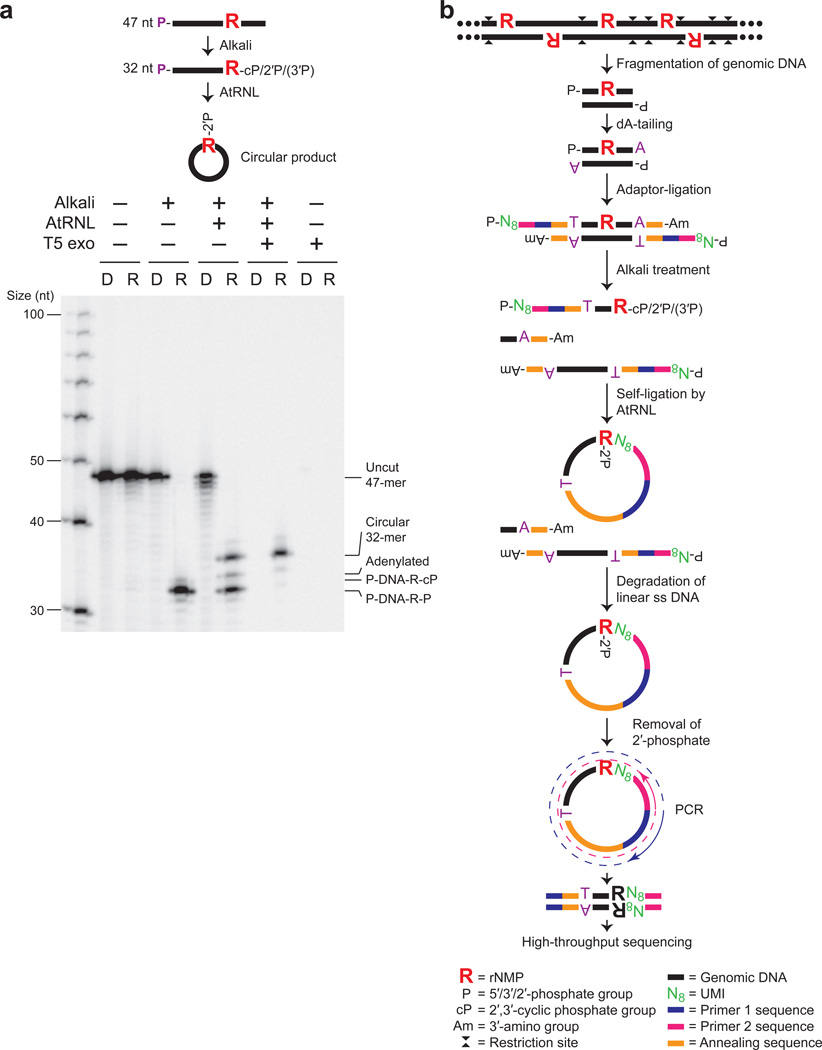
Figure 1. Ribose-seq method for mapping rNMPs in genomic DNA.
(a) AtRNL captures 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate or 2′-phosphate DNA termini generated by alkaline cleavage of a single rGMP in a 5′-radiolabeled 47-nt ss DNA oligo (see Supplementary Table 8). R, rGMP or rGMP-bearing oligo. D, DNA-only control oligo. P, 5′-radiolabel. T5 exonuclease treatment confirms the presence of circular ligation product. Left lane, ss DNA ladder. Ligation efficiency was about 50%, as expected due to the mixture of 2′-phosphate and 3′-phosphate ends generated upon alkaline cleavage. (b) Schematic of Ribose-seq protocol. Genomic DNA is fragmented, dA-tailed and ligated to a molecular barcode-containing sequencing adaptor. Alkali treatment denatures the DNA and cleaves at rNMP sites, exposing 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate and 2′-phosphate termini, which are self-ligated to 5′-phosphate ends by AtRNL. Linear, unligated fragments are degraded by T5 exonuclease while the remaining rNMP-captured, circular DNA molecules, upon removal of 2′-phosphate at the ligation junction by 2′-phosphotransferase Tpt1, are PCR-amplified and sequenced.