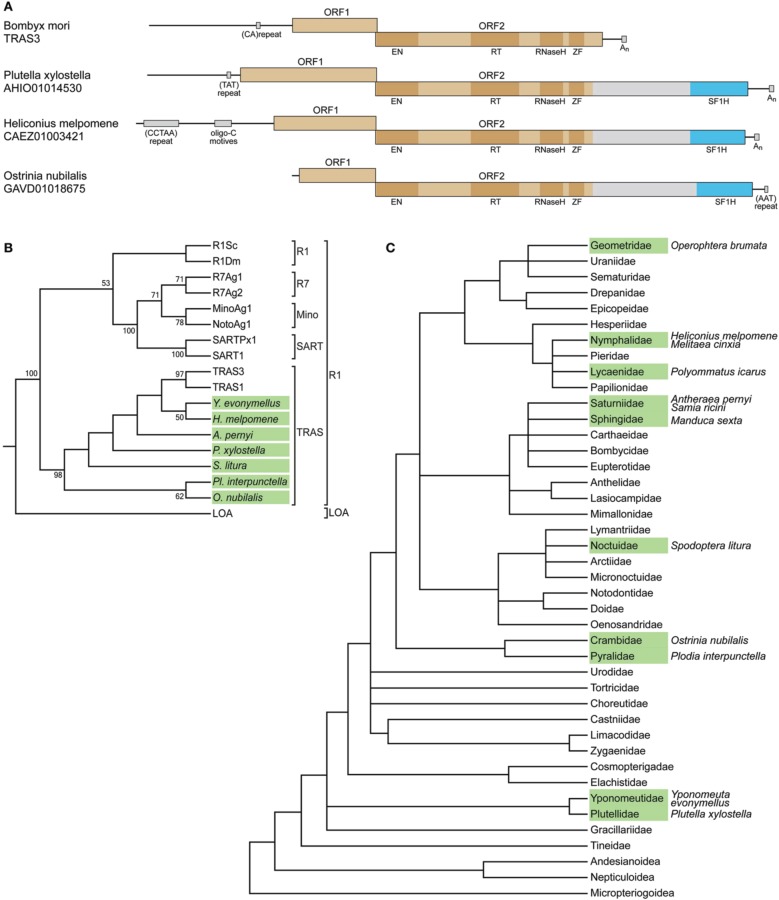
Figure 1.
SF1H domains in insect genomes. (A) SF1H domains encoded by insect LINEs. Organization of three insect LINEs encoding tobamovirus-like SF1H domains and closely related Bombyx mori LINE TRAS3. Boxes schematically represent open reading frames ORF1 and ORF2. Blue boxes represent the tobamovirus-like SF1H domains. Functional domains in ORF2 are indicated by dark boxes. EN, endonuclease domain; RT, reverse transcriptase domain; ZF, zinc finger domain. Conserved DNA sequence signatures outside ORF1/ORF2 region are indicated by small boxes. (B) SF1H-encoding LINEs belong to the TRAS superfamily of the R1 clade of LINEs. The phylogenetic tree is based on RT domain amino acid sequence alignment generated for SF1H-encoding LINEs and other LINEs. Seven species with SF1H-encoding LINEs, for which RT domain sequences are available, were included into the analysis. Insect species with SF1H-encoding LINEs are show in green. Conventional names for previously known LINEs are given. Clades R1 and LOA are indicated on the right. Superfamilies within the R1 clade are shown. Only bootstrap values ≥50% are shown. (C) Occurrence of SF1H-encoding LINEs in different families of Lepidoptera. The tree represents the synoptic view of the phylogeny of major Lepidoptera taxa (Wheeler et al., 2013). Families for which SF1H-encoding LINEs were identified are shown in green. Species with SF1H-encoding LINEs are indicated on the right.