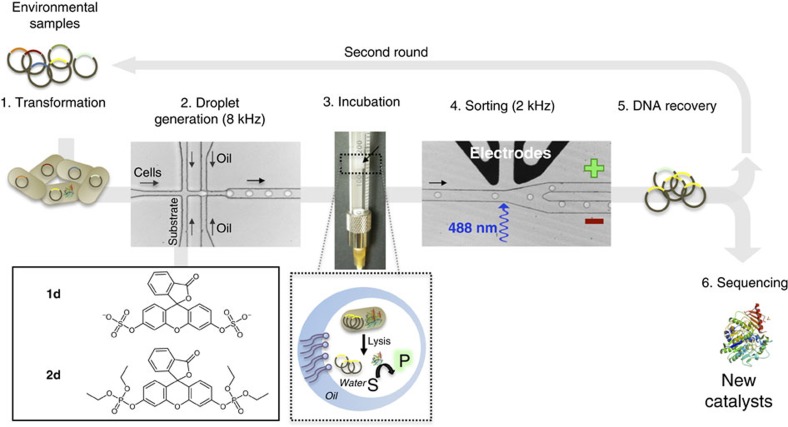
Figure 1. Functional metagenomic using microfluidic droplets.
General procedure. (1) Environmental DNA (eDNA) was cloned into a high-copy plasmid and transformed into E. coli. (2) Single bacteria were encapsulated into water-in-oil droplets together with substrate (1d or 2d) and lysis agents. (3) Emulsion droplets were incubated off-chip; after single cell lysis, cytoplasmically expressed protein catalysts were able to turn over substrate. The arrow designates the droplets (∼3 × 107) at the interface between fluorous oil and mineral oil (on top). (4) Emulsion droplets were re-injected (Supplementary Movie 1) into a sorting chip and strongly fluorescent droplets (‘+' channel) were separated from those with fluorescence below the threshold (‘−' channel) by dielectrophoresis24 (Supplementary Movie 2). (5) Selected droplets were de-emulsified and high-copy plasmid DNA was recovered following by re-transformation into E. coli. For further enrichment, iterative selections could be performed. (6) Plasmids containing eDNA coding for active catalysts were sequenced. The microfluidic devices are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5.