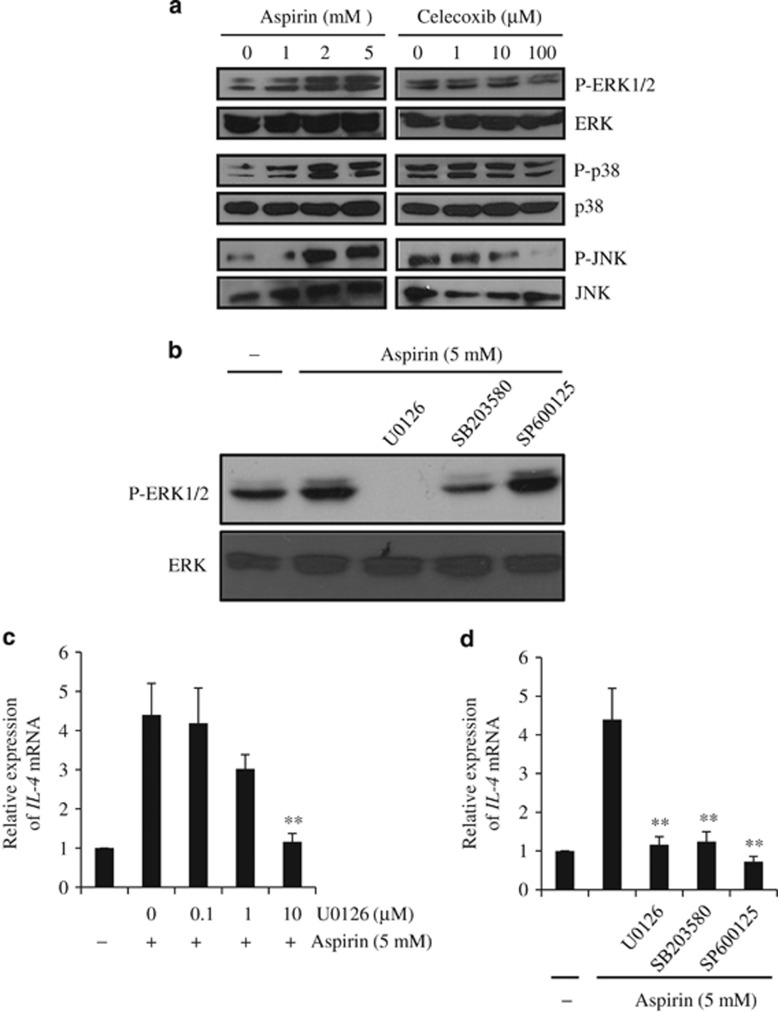
Figure 3.
Interleukin (IL-4) mRNA expression requires the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). (a) HMC-1 cells were treated with aspirin or celecoxib for 4 h. Activation of MAPKs was then assessed by western blotting. The blots were probed with anti-phospho-MAPK antibodies (Abs). Replica blots were probed for total MAPKs as loading controls. (b) HMC-1 cells were treated with aspirin (5 mM) for 4 h following pretreatment with U0126 (10 μM), SB203580 (10 μM) or SP600125 (20 μM) for 30 min. The blots were probed with anti-phospho-ERK1/2 Ab and reprobed with anti-total ERK Ab as a loading control. (c) HMC-1 cells were treated with aspirin (5 mM) for 4 h following pretreatment with increasing doses of U0126 or for 30 min. IL-4 expression was then assessed by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). (d) HMC-1 cells were pretreated with U0126 (10 μM), SB203580 (10 μM) or SP600125 (20 μM) for 30 min before treatment with aspirin for 4 h. IL-4 expression was then quantified by qPCR. The data (mean±s.e.m., n=3) are expressed relative to the PP1A mRNA levels (**P<0.01 compared with aspirin-treated cells). ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase.