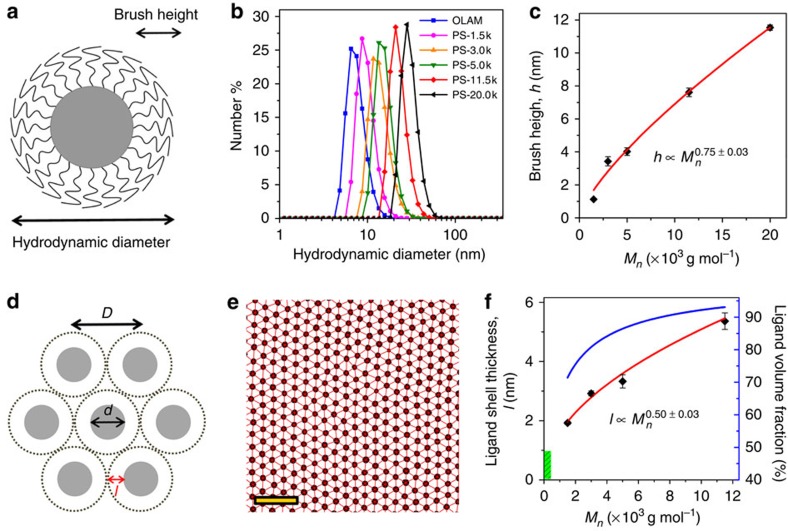
Figure 1. Scaling behaviour of polymer brushes on spherical NCs.
(a) Schematic illustration of NCs end-grafted with polymer brushes in good solvents. (b) Plots of number-averaged hydrodynamic diameter and (c) scaling relation of DLS-derived brush height, h, as a function of the molecular weight of thiol-terminated polystyrene ligands for 7.6 nm Au NCs dispersed in toluene. (d) Schematic showing the relationship between D, the centre-to-centre distance between nearest-neighbour NCs, d, the diameter of the inorganic core of the NCs, and the ligand shell thickness, l=(D−d)/2, for two-dimensional hexagonal NC superlattices. (e) Particle tracking analysis of TEM images for statistical determination of average nearest-neighbour interparticle distance D. A sample area of two-dimensional assemblies of 7.6 nm Au NCs is shown. Scale bar, 50 nm. (f) Scaling relations of ligand shell thickness l, and calculated ligand volume fraction (blue curve) as a function of molecular weight for 7.6 nm Au NCs in the dried state. The green area highlights the range of Mn and l accessible by using commonly employed alkyl ligands. The ligand volume fraction is computed as 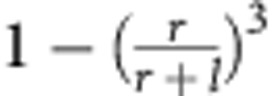 , where r=d/2. The red curves in c and f represent the best fit to the data using a power-law function.
, where r=d/2. The red curves in c and f represent the best fit to the data using a power-law function.