Figure 1.
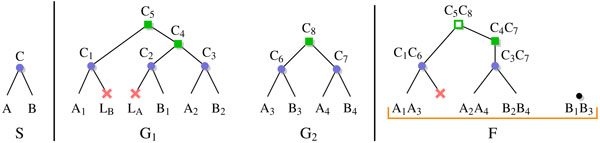
Example of an adjacency forest predicted from two reconciled gene trees. (Left) Species tree S, with two extant species A and B and an ancestral species C. (Middle) Two reconciled gene trees G1 and G2, with four extant genes in genome A, four extant genes in genome B and three ancestral genes in genome C. The set of extant adjacencies is (A1A3, B1B3, A2A4, B2B4) (Right) Parsimonious adjacency forest F composed of two adjacency trees. Blue dots are speciation nodes. Leaves are extant (species, genes, adjacencies), except when labelled with a red cross (gene loss). Green squares are (gene or adjacency) duplication nodes. Gene labels refer to the species of nodes. Every node of the adjacency tree is labelled by a couple of nodes from gene trees. Figure adapted from [5].
