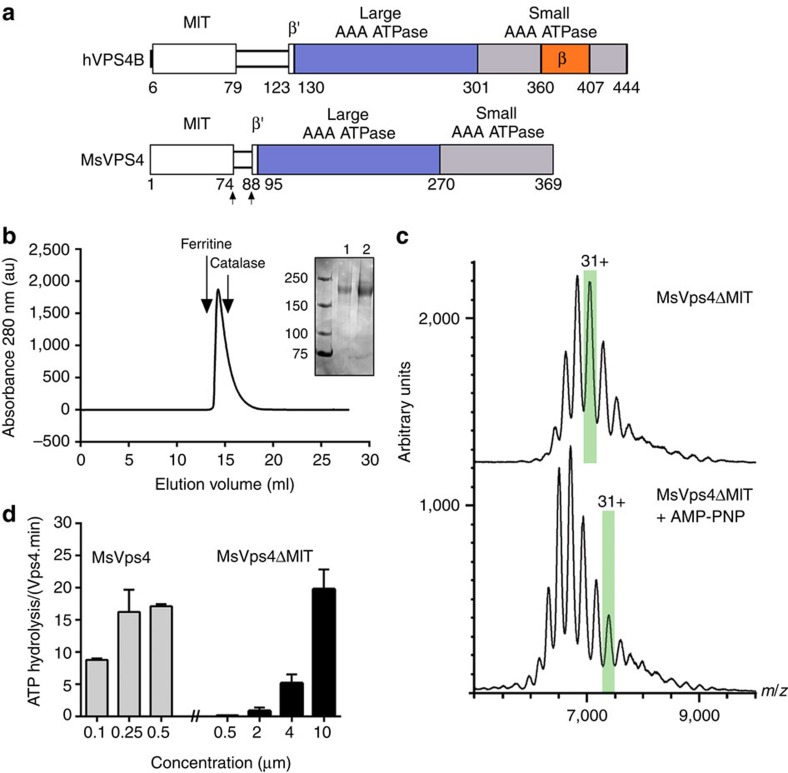
Figure 1. Biochemical and enzymatic analysis of recombinant MsVps4ΔMIT.
(a) Domain organization of hVPS4B and MsVps4. MsVps4 was expressed as wild type or with N-terminal deletions (residues 75–369 and residues 88–369). (b) Elution profile of MsVps4ΔMIT (200 μM) from a Superose 6 SEC column. The elution peak of molecular sizing markers ferritin (450 kDa) and catalase (250 kDa) are indicated. Insert: SDS–PAGE analysis of MsVps4ΔMIT cross-linked with glutaraldehyde in the absence (lane 1) and the presence (lane 2) of 1 mM AMP-PNP and 1 mM Mg acetate. Hexamer formation was confirmed by native mass spectrometry. (c) Mass spectra of the cross-linked MsVps4ΔMIT in the absence (top spectrum) and the presence of AMP-PNP (bottom spectrum). MsVps4ΔMIT is hexameric in both conditions. The mass of MsVps4ΔMIT in the presence of AMP-PNP is larger than in the absence of the non-hydrolysable ATP analogue. This greater mass is most likely to be due to a covalent binding of the AMP-PNP. The ions carrying 31 charges (31+), highlighted in green, illustrate the mass difference between the two samples. (d) ATP hydrolysis of full-length MsVps4 and MsVps4ΔMIT at 60 °C. Values reported represent mean±s.d. of three independent experiments carried out on at least two different batches of purified Vps4.