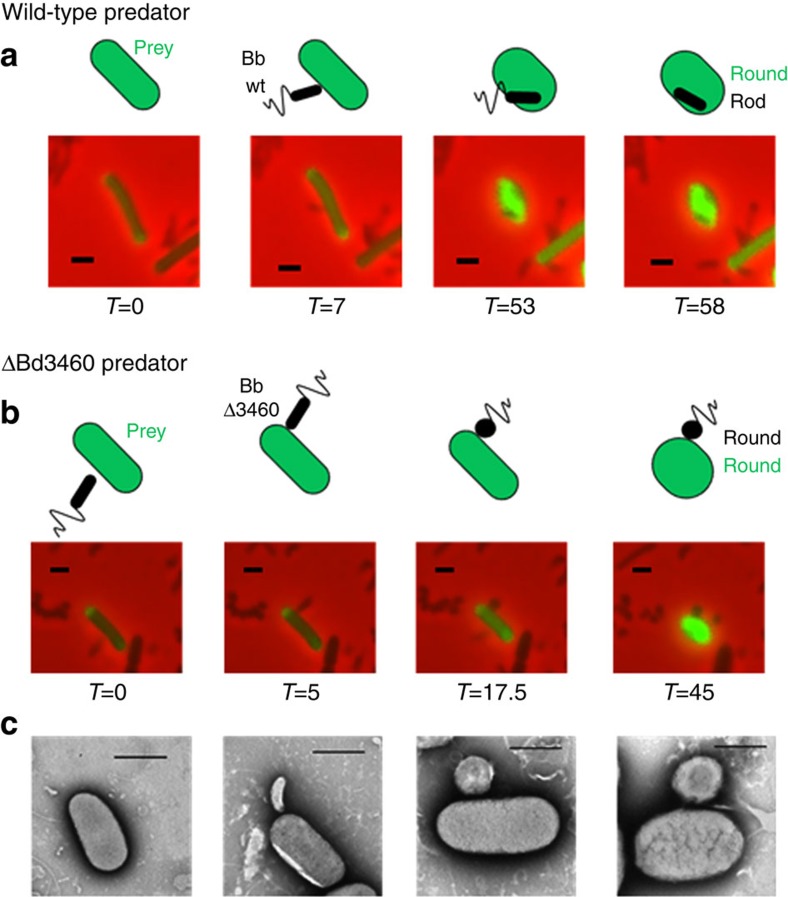
Figure 3. ΔBd3460 Bdellovibrio self-round upon initiating prey cell entry.
Epifluorescence phase contrast microscopy of Bdellovibrio (small, phase dark, comma-shaped cells) preying upon E. coli prey cells which have periplasms constitutively fluorescently labelled by a pMal::mCherry fusion. A cartoon representation is presented above each. (a) Control using host independent strain HID22 which is wild-type for Bd3460 (Bb wt) and shows typical attachment to and entry into the prey cell which is rounded up in the process. (b) ΔBd3460 host independent strain (Bb Δ3460) attaches to the prey cell in a manner similar to the wild-type control, but then rounds up itself, preventing entry into the prey cell. (c) Representative electron micrographs showing the different stages of attachment, Bdellovibrio rounding, and prey rounding. Scale bars, 1 μm ; time is indicated in minutes.