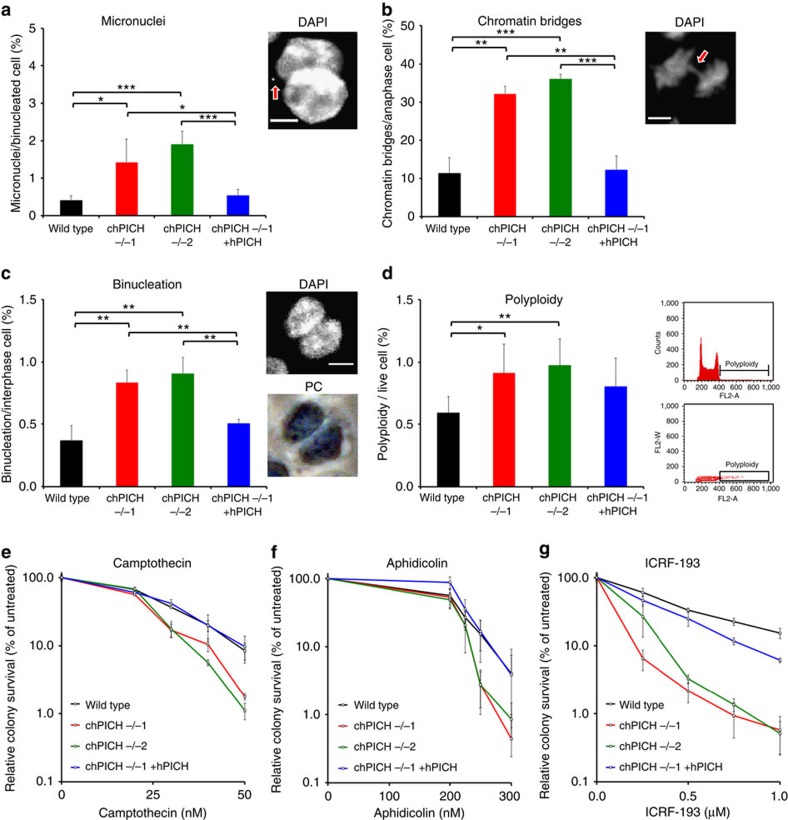
Figure 3. Chromosomal instability and drug sensitivity of PICH−/− cells.
(a) Frequency of micronucleus formation in binucleated cells arrested at cytokinesis with cytochalasin B and stained with DAPI. An example of a scored micronucleus is shown (red arrow). (b) Frequency of chromatin bridge formation in anaphase cells stained with DAPI. An example of a scored bridge is shown (red arrow). (c) Frequency of binucleation in asynchronously growing cells stained with DAPI and imaged by fluorescence and phase contrast microscopy. An example of a scored binucleated cell is shown. (a–c) Scale bars, 5 μm. (d) Frequency of polyploidy in cells stained with propidium iodide. Cells with a greater than G2/M DNA content were quantified using FACS. An example of a FACS profile is shown with the position of polyploid cells marked. Examples of profiles for all cell lines are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1a. The setting used for gating away dead cells and aggregates is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1b. In all cases, each data point is an average of at least three independent experiments ±s.d. Significance levels were determined using the Student's t-test for parametric observations, and are indicated as *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (e–g) Clonogenic survival assays. Cells of the indicated genotypes were exposed continuously to camptothecin (e), aphidicolin (f) or ICRF-193 (g). Each data point is the average of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate ±s.d.