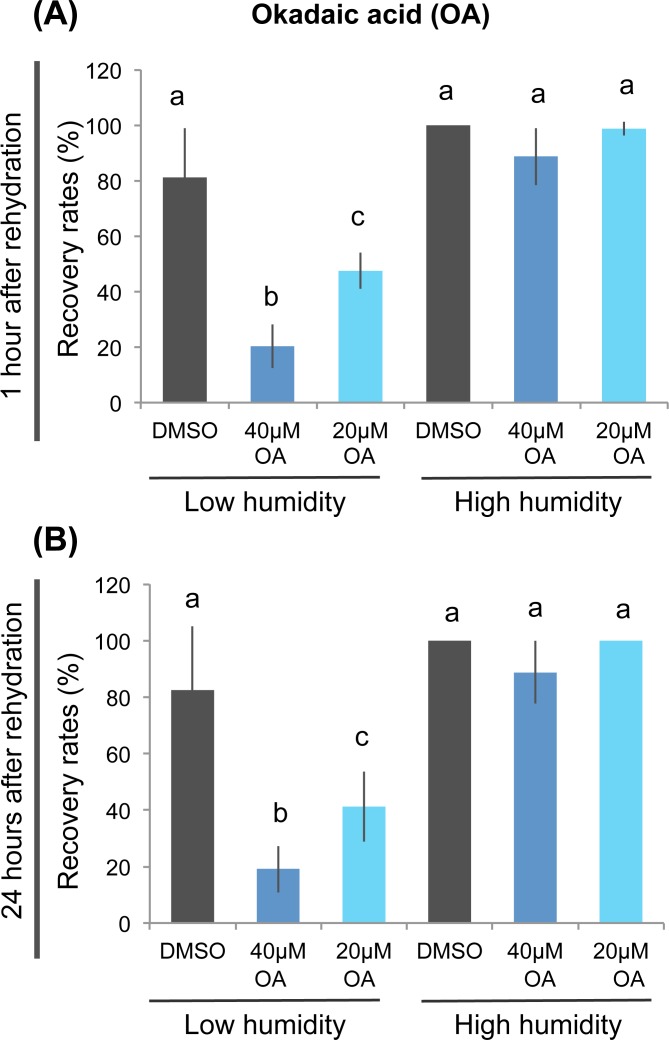
Fig 5. Inhibition of PP1/PP2A activity impaired anhydrobiotic survival.
The effects of another potent PP1/PP2A inhibitor, okadaic acid, on anhydrobiotic survival were examined using essentially the same scheme shown in Fig 2A, with a longer chemical treatment period (10 h). Either 40 μM or 20 μM okadaic acid specifically inhibited recovery rates after low humidity exposure at both 1 h (A) and 24 h (B) after rehydration. Mean ± SD (N = 4; 20 tardigrades each). Statistically significant differences among samples were determined by the Tukey-Kramer test. Different letters indicate significant differences (P<0.01). Low humidity, low humidity exposure; High humidity, high humidity exposure.