Figure 1. Structural changes in gluten proteins by transamidation of wheat flour and gluten under non-reducing conditions.
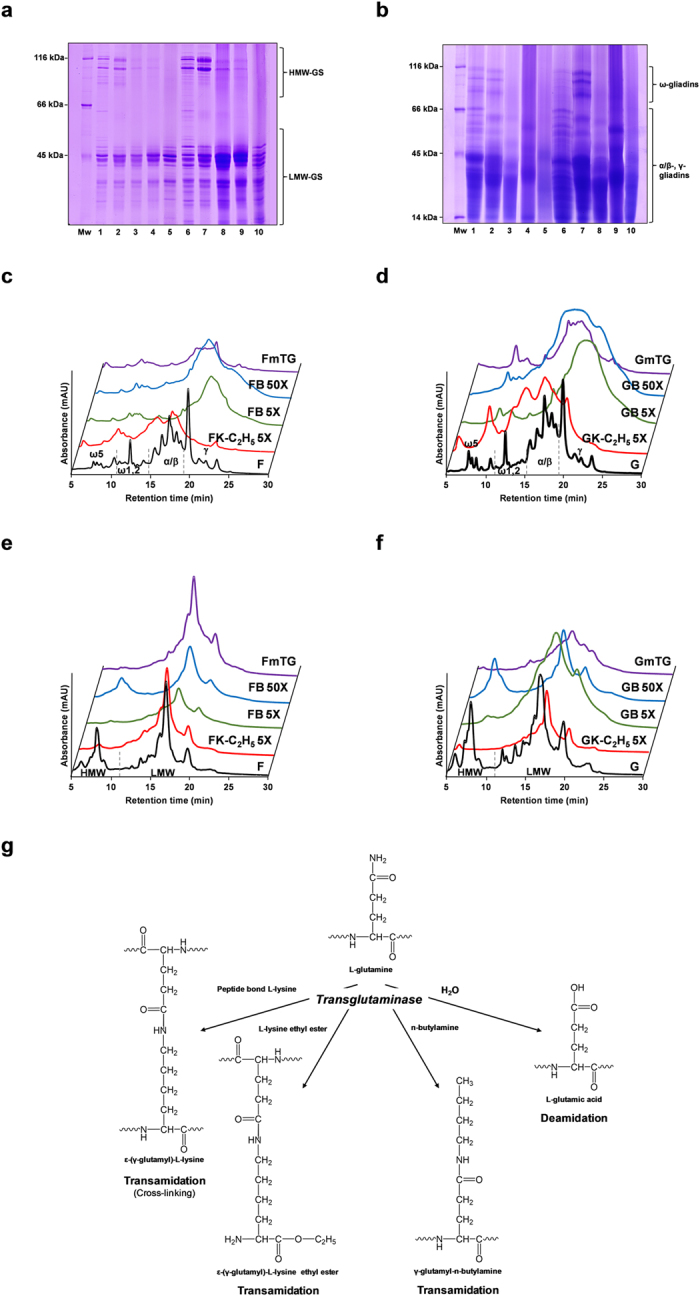
(a) Reduced and alkylated glutenin subunit electrophoretic patterns of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions. (b) Gliadin electrophoretic patterns of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions. Lane 1, F; Lane 2, FB 50X; Lane 3, FB 5X; Lane 4, FK-C2H5 5X; Lane 5, FmTG; Lane 6, G; Lane 7, GB 50X; Lane 8, GB 5X; Lane 9, GK-C2H5 5X; Lane 10, GmTG. Reversed-phase HPLC results for gliadins (c,d) and glutenins (e,f) extracts of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions. Wheat flour chromatograms are represented for a maximum absorbance of 1.0 and gluten chromatograms are represented for a maximum absorbance of 2.5. ω5, ω1,2, α/β and γ represent the different identified gliadin proteins, and HMW and LMW represent the different glutenin subunits. Absorbance was registered at 210 nm. For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6. (g) Reactions catalysed by microbial transglutaminase and the end-products.
