Figure 2. Cross-linking of gluten decreases toxic epitopes amount and affect negatively the rheological properties of gluten.
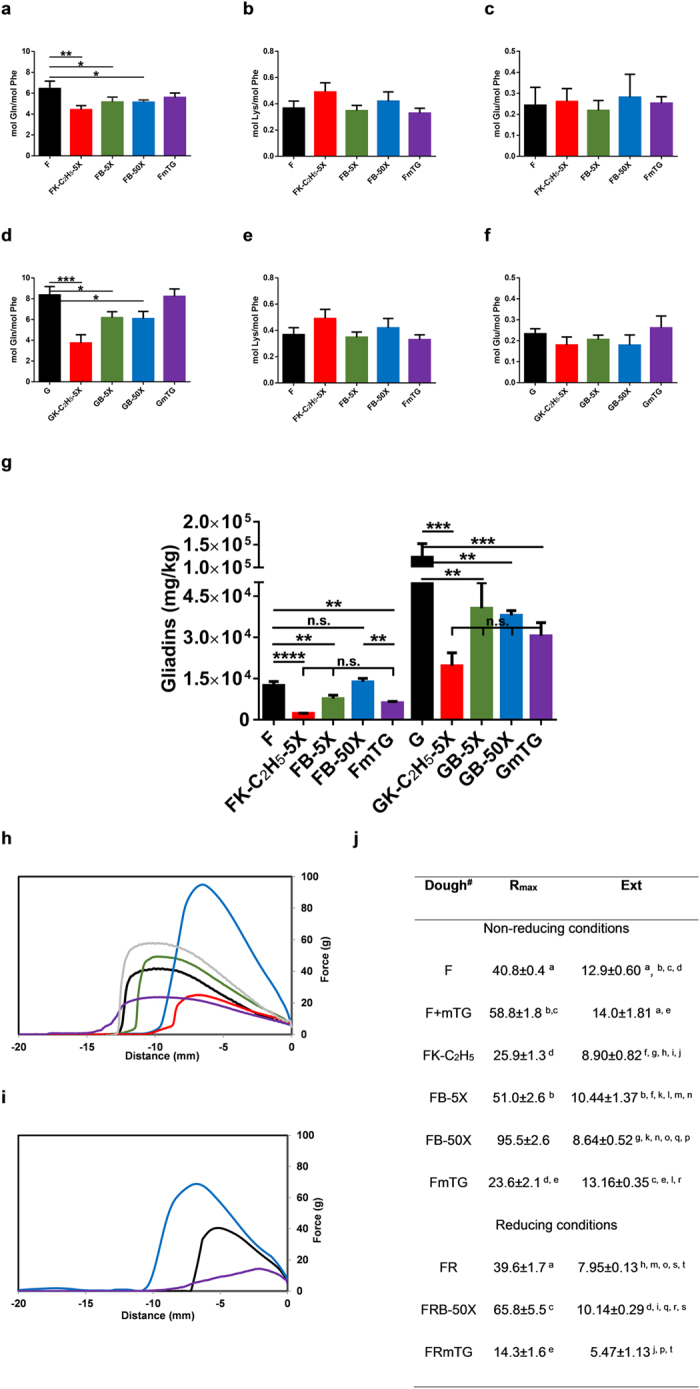
Amino acid composition determined after enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat flour (a–c) and gluten (d–f), original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions. For (a–f) error bars represent the standard deviation *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 (n = 3). (g) R5 reactive epitopes’ content (mg of gliadin per kg of product) of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions after peptic-tryptic digestion. n = 2 different experiments (each with four replicates) and error bars represent the s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. Micro-extension tests with dough prepared from wheat flour, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing conditions. (h):  F;
F;  FK-C2H5;
FK-C2H5;  FB 5X;
FB 5X;  FB 50X;
FB 50X;  FmTG;
FmTG;  F + mTG. Or, under reducing conditions. (i):
F + mTG. Or, under reducing conditions. (i):  FR;
FR;  FRB 50X;
FRB 50X;  FRmTG. (j) Rheological properties of dough prepared from wheat flour, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing and reducing conditions. #For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6. The columns values with the same letter are not statistically significant, p < 0.05 (n = 2).
FRmTG. (j) Rheological properties of dough prepared from wheat flour, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing and reducing conditions. #For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6. The columns values with the same letter are not statistically significant, p < 0.05 (n = 2).
