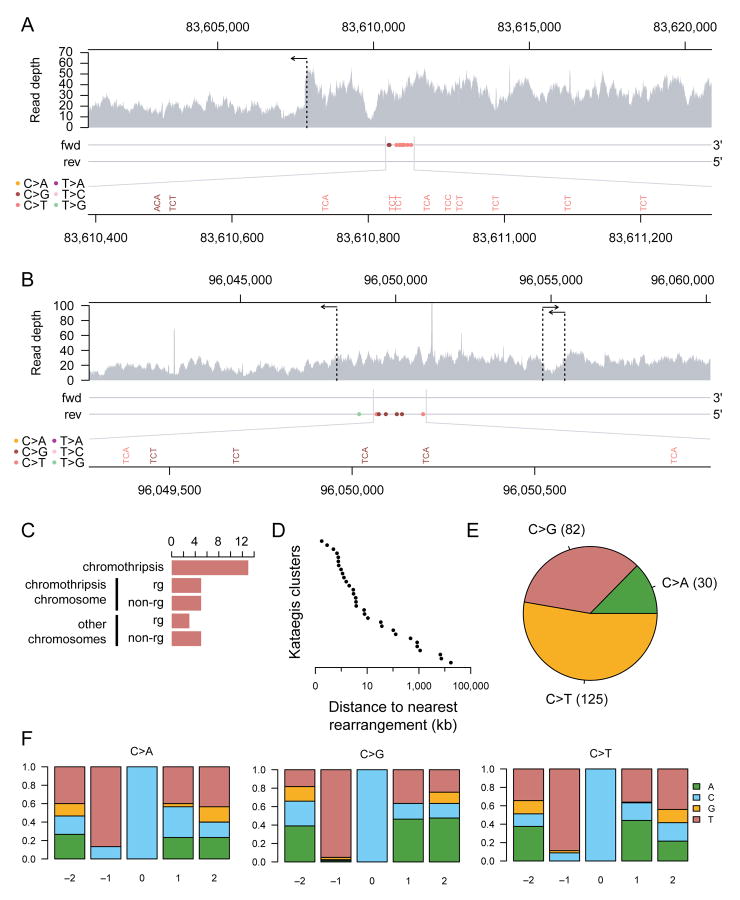
Figure 6. Mutational patterns of kataegis in post-crisis clones.
(A) A chromothripsis-associated kataegis in sample 24-141 on chromosome 7.
(B) A kataegis event in sample X-25 on chromosome X. This kataegis event took place on a chromosome with evidence for chromothripsis, but the rearrangements associated with the kataegis event do not appear to be part of the chromothripsis (Figure 5B). For both (A) and (B), the top panel shows raw read coverage of the region. The horizontal arrows indicate the positions of rearrangements. The two horizontal lines in the middle panel represent the forward and reverse strands. The pyrimidine strands of the mutations called are indicated by their placement on one of the two strands. Mutations are colored by mutation type. The bottom panel magnifies the mutation cluster regions and shows mutation contexts.
(C) The number of kataegis events grouped by their association with rearrangements as follows. From top to bottom: kataegis events within 10 kb of a chromothripsis rearrangement; kataegis events on a chromothripsis chromosome within 10 kb of a non-chromothripsis rearrangement; kataegis events on a chromothripsis chromosome with no rearrangements within 10 kb; kataegis events on a non-chromothripsis chromosome within 10 kb of a rearrangement; and kataegis events on non-chromothripsis chromosome with no rearrangements within 10 kb.
(D) The distance of each of the 31 detected kataegis events to their nearest respective rearrangement breakpoint.
(E) The frequency distribution of mutation types in the detected kataegis clusters.
(F) The nucleotide context around the mutated cytosine grouped by cytosine mutation type. The relative positions shown are on the pyrimidine (cytosine) strand. The Y-axes show the fraction of each nucleotide on the pyrimidine strand.
See also related Figure S7.