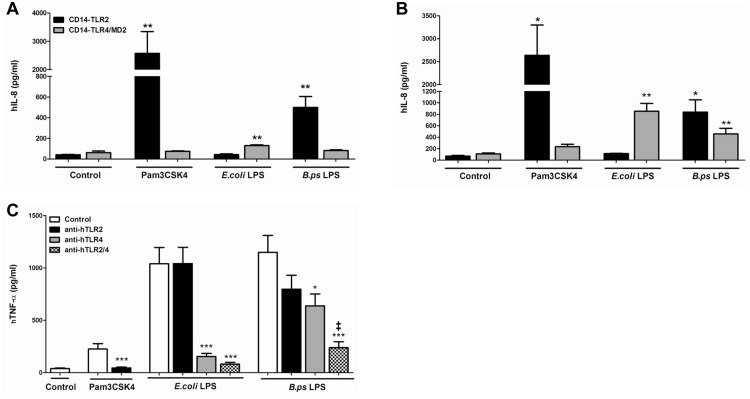
Fig 2. LPS of B.pseudomallei signals via both TLR2 and TLR4 in in vitro human models.
Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK)-293 cells, stably transfected with either CD14-TLR2 or CD14-TLR4/MD2 were stimulated with purified LPS of B.pseudomallei 1026b (100 ng/ml), LPS of E. coli 0111:B4 (100 ng/ml), PAM3CSK4 (100 ng/ml) or DMEM+ 10% FCS for 6h (A) or 24h (B) before measurement of interleukin (IL)-8 in the supernatant (n = 3). Human whole blood was pre-treated for 30 minutes with respectively RPMI 1640 medium, anti-TLR2 antibody (2500 ng/ml), anti-TLR4 antibody (1000 ng/ml) or both antibodies and hereafter stimulated with purified LPS of B.pseudomallei 1026b (100 ng/ml), LPS of E. coli 0111:B4 (100 ng/ml), PAM3CSK4 (100 ng/ml) or RPMI 1640 for 6h after which TNF was measured (C) (n = 3). An additive effect of TLR2 on TLR4 mediated signalling induced by B.pseudomallei-LPS was observed. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Results of two or three independent experiments were pooled. Mann-Whitney- U tests were performed. *P< 0.05; **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001 vs. control (or no antibodies). ‡ P< 0.05 anti-TLR2 and 4 vs. anti-TLR4 alone.