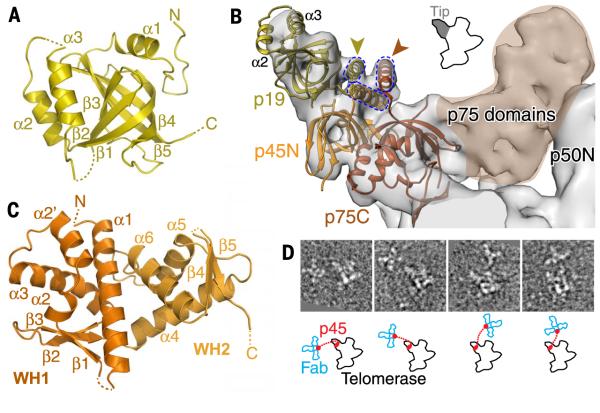
Fig. 5. Identification of p75-p45-p19 as a Tetrahymena CST complex.
(A) Crystal structure of p19, an OB fold. (B) Model of p75C-p45N-p19 based on fitting of RPA70C-RPA32N-RPA14 into the 9.4 Å cryo-EM map, followed by replacement of RPA14 by p19, except for the RPA14 C-terminal helix. p19 α2 and α3 account for the density at the end of the tip. Gold and orange arrowheads point to the locations of the p19 and p75 C termini, respectively, previously determined by Fab labeling in negative-stain EM (29). The three-helix bundle between the C-terminal residues of p75, p45N, and p19 (modeled from RPA) is illustrated with dashed lines. (C) Crystal structure of p45C, a WH-WH domain. β5 is domain-swapped from a neighboring protein in the crystal lattice. (D) (Top) Negative-stain EM images of four typical p45-Fab–labeled telomerase holoenzyme particles, showing a cluster of 3 Fab bound to the C terminus of p45 at various locations near the holoenzyme. The side length of each image box is 44 nm. (Bottom) Corresponding outlines of telomerase and Fabs are shown in black and blue, respectively. Red dots indicate the p45C (attached to 3 Fab) and p45N (on telomerase) domains; dotted lines represent the linker.