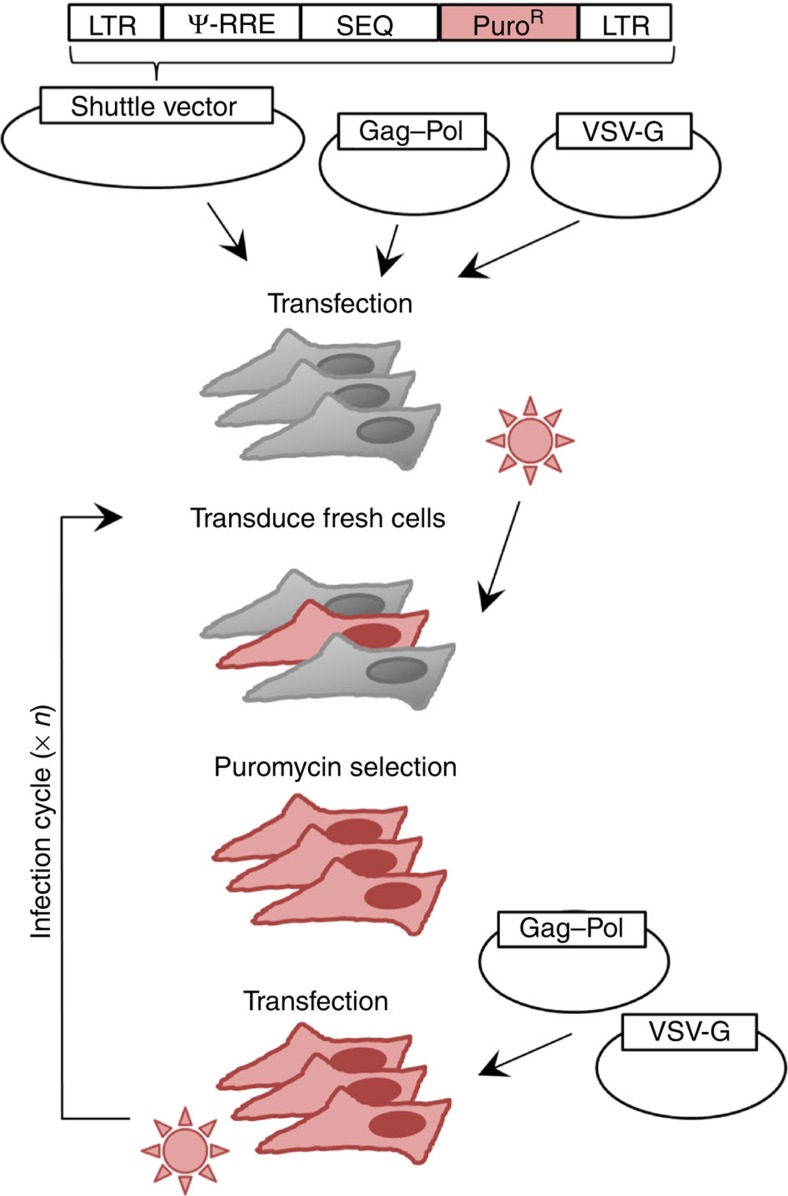
Figure 1. HIV-1 shuttle vector system used for scoring spontaneous mutations.
A scheme of the system used for serial passaging of HIV-1 sequences in the absence of selection is shown. The shuttle vector contains the necessary elements for genomic integration (LTR) and efficient packaging (Ψ element and Rev-responsible element (RRE)), as well as the puromycin resistance gene to enable selection of cells in which integration occurs. The inserted sequence (SEQ, here env or int–vif–vpr) is carried forward by the vector. Translation of the Gag p17 protein starts at position 335 of our genomic RNA but, since a 2-nt insertion was introduced at position 355, the sequence rapidly falls out of frame and the SEQ insert is thus located many stop codons away from this translation initiation site (position 1,950). Translation could not start elsewhere because there is no internal ribosome entry site (IRES). The production of a protein from a spliced version of the genomic RNA is also excluded because, although the major HIV-1 splice donor site is present at position 289 of the vector, there are no splice acceptor sites in the inserted env sequence. Four acceptor sites are present in the int–vif–vpr sequence, but no protein synthesis can occur because of lack of initiating codons. The HIV-1 proteins Gag and Pol and the VSV envelope protein G are instead expressed from two helper plasmids. Initial transfection of the three plasmids is required to recover pseudotyped viruses, which are transduced into fresh cells where they undergo integration. The infection cycle can be restarted by transfecting the two helper plasmids only. After a given number of cycles, the DNA of the insert can be PCR-amplified from puromycin-selected cells, cloned, and sequenced. The inserted sequences contain no known functional cis-acting elements or RNA structures except for the RRE, which is required for nuclear export of viral RNA and is embedded in the env gene. However, this element was provided redundantly from the vector, thus minimizing selection. Recombination between vector (subtype B) and insert (subtype A) RRE copies was checked, and recombinant sequences were discarded from the analysis.