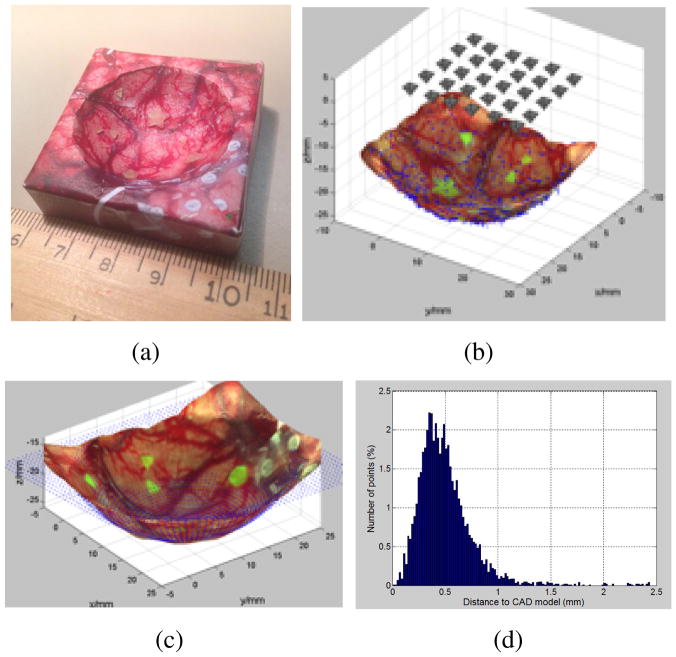
Fig. 1.
The 3D reconstruction of a spherical tumor cavity phantom with surgical image and residual fluorescence tumor targets. (a). A 3d printed phantom with texture of brain surgery photo glued on its surface. (b) Image sampling grid 5×6 above phantom. (c) The comparison of reconstructed 3D model to the CAD model, shown as blue point cloud. (d). The ICP error between the reconstructed model and the CAD design. 96.3% of all the error values locate in the range of [0–1] mm.