Figure 3.
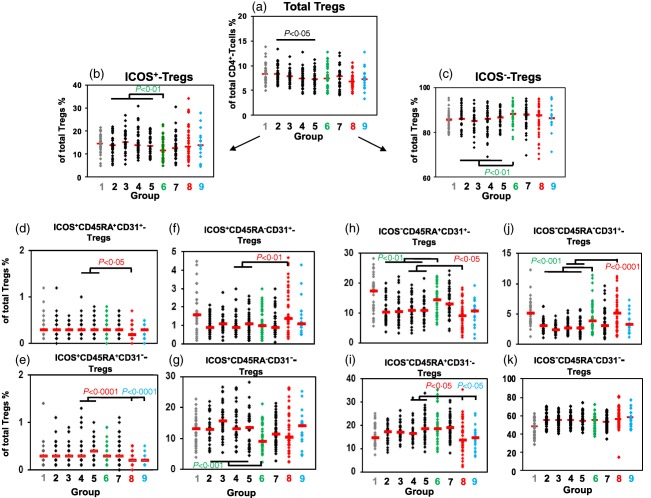
Detection of inducible co‐stimulatory (ICOS)+ and ICOS−CD45RA+CD31+ recent thymic emigrant (RTE) regulatory T cells (Tregs), ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA+CD31− mature naive (MN) Tregs, ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA−CD31+ memory Tregs and ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA−CD31− memory Tregs within the total CD4+CD127low+/−forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3)+ Treg pool during the normal pregnancy course and in the presence of pre‐eclampsia and haemolysis elevated liver enzymes low platelet (HELLP) syndrome. The percentage of total CD4+CD127low+/−FoxP3+ Tregs within CD4+ T cells (a), the percentages of ICOS+ (b) and ICOS− Tregs (c), ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA+CD31+ RTE Tregs (d,h), ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA+CD31− MN Tregs (e,i), ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA−CD31+ memory Tregs (f,j) and ICOS+ and ICOS−CD45RA−CD31− memory Tregs (g,k) within the total CD4+CD127low+/−FoxP3+ Treg pool were determined in healthy non‐pregnant fertile women (group 1,  ), healthy pregnant women during their pregnancy course (groups 2–5, ◆), spontaneously term labouring women (group 6,
), healthy pregnant women during their pregnancy course (groups 2–5, ◆), spontaneously term labouring women (group 6,  ), 1 day postpartum (group 7, ◆) and in women with pre‐eclampsia (group 8,
), 1 day postpartum (group 7, ◆) and in women with pre‐eclampsia (group 8,  ) or HELLP syndrome (group 9,
) or HELLP syndrome (group 9,  ). Significant differences concerning the percentages of the different Treg subsets were detected between women during the normal pregnancy course (groups 2–5) and non‐pregnant women (group 1) or women with spontaneous term labour (group 6). In addition, significant differences were detected between healthy third‐trimester women (groups 4 and 5) and women with pre‐eclampsia (group 8) or HELLP syndrome (group 9).
). Significant differences concerning the percentages of the different Treg subsets were detected between women during the normal pregnancy course (groups 2–5) and non‐pregnant women (group 1) or women with spontaneous term labour (group 6). In addition, significant differences were detected between healthy third‐trimester women (groups 4 and 5) and women with pre‐eclampsia (group 8) or HELLP syndrome (group 9).
