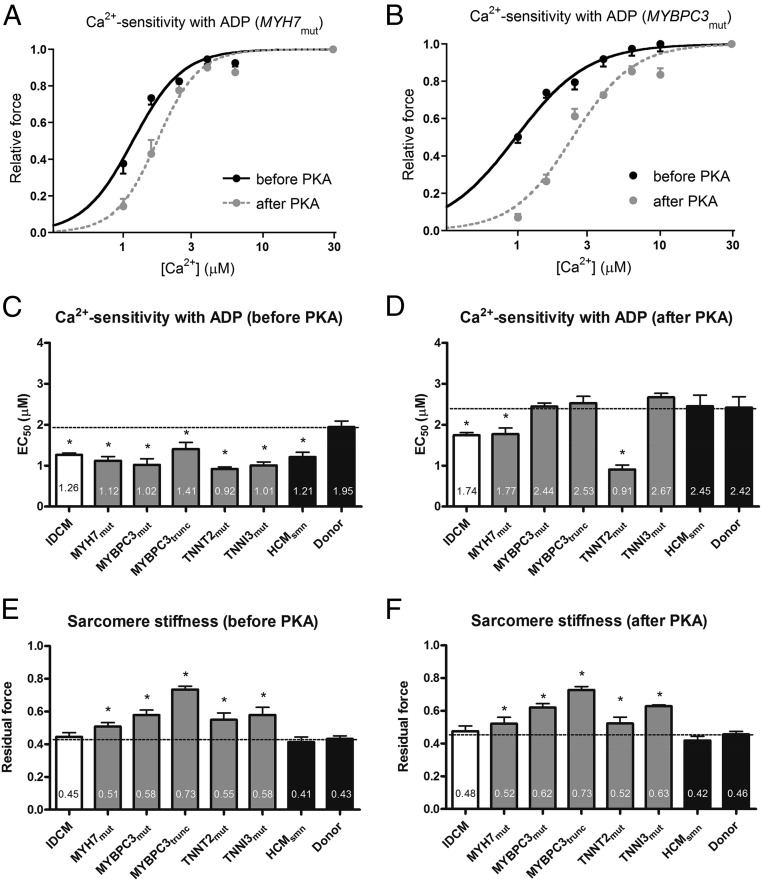
Fig. 5.
Myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity and sarcomere stiffness, in the presence of 100 µM ADP, in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDCM) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) membrane-permeabilized cardiomyocytes. Normalized force–Ca2+ relationships before and after protein kinase A (PKA) in the presence of ADP for MYH7mut (A) and MYBPC3mut (B) heart samples. Myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in the presence of ADP (EC50) before (C) and after (D) PKA treatment in IDCM, HCM, and donor samples. Residual force, a measure of sarcomere stiffness, at high Ca2+ with 100 µM ADP (EC50) before (E) and after (F) PKA treatment in IDCM, HCM, and donor samples. Data were compared using multilevel analysis. N, number of samples; n, number of cardiomyocytes. HCMsmn, sarcomere mutation-negative HCM samples (n = 3, n = 8); IDCM (n = 4, n = 18); MYBPC3mut, myosin-binding protein-C (missense) mutations (n = 3, n = 10); MYBPC3trunc, myosin-binding protein-C (truncating) mutations (n = 4, n = 12); MYH7mut, myosin heavy-chain mutations (n = 3, n = 10); TNNI3mut, cardiac troponin I mutation (n = 1, n = 4); TNNT2mut, cardiac troponin T mutation (n = 1, n = 4). Fourteen cardiomyocytes from five nonfailing hearts (donor) served as controls.