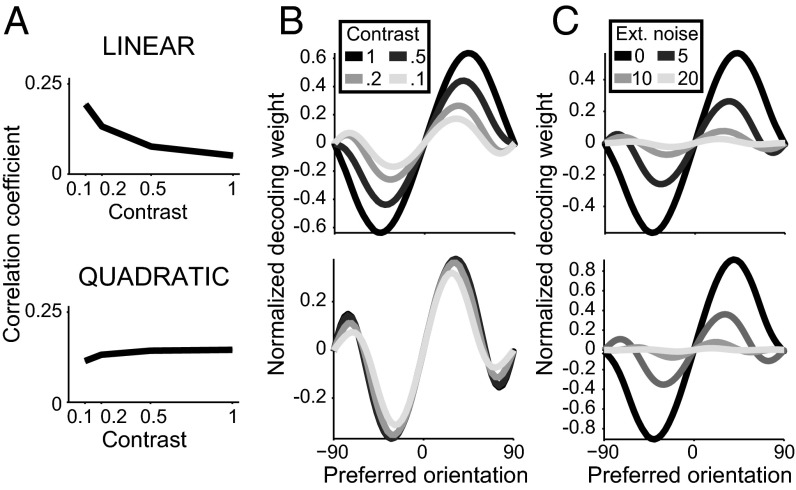
Fig. 4.
Optimal decoding with linear and quadratic V1 models. (A) Noise correlations depend on image contrast in the linear model (Top), but are approximately contrast invariant in the quadratic model (Bottom). (B) Weights of the locally optimal decoder of orientation around 0° plotted as a function of the preferred orientation of each neuron. The optimal linear decoder depends on image contrast in the linear model (Top), but is contrast independent in the quadratic model (Bottom). (C) The locally optimal linear decoder depends on the amount of noise added at the sensory periphery in both models. In B and C the normalization convention for the decoding weights is wnorm = wopt FI = Σ−1 f′, where Σ is the covariance matrix and f′ is the derivative of the tuning curves (Methods and SI Appendix, section 5). Note that the decoding weights in both models are smooth despite heterogeneous tuning. Simulation parameters are specified in SI Appendix, Table S4.