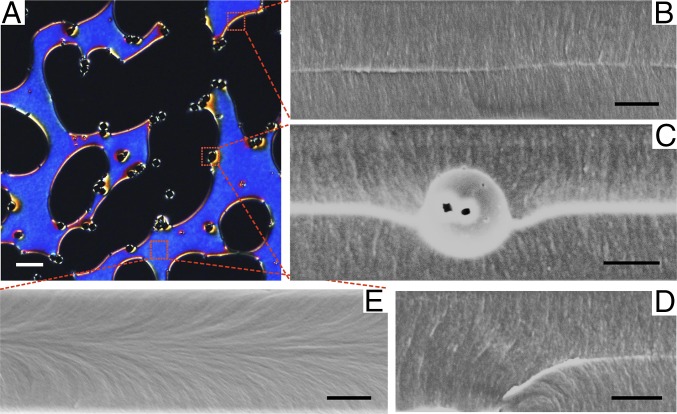
Fig. 6.
Metastable configurations. (A) POM image of silica colloids suspended in LCM resulting in coexistence of homeotropic and planar-like regions, where the metastable planar regions (blue color) are stabilized by silica colloids. (B, C, and E) SEM images characterizing the local director field at different positions in A as indicated by the red dotted squares. (B) SEM image taken at the boundary between homeotropic and planar regions of LC, where a bright line in the middle of the image is shown, indicating the presence of a disclination line. (C) SEM image of a silica colloid sitting at the boundary. The bright line in the image shows a line defect in the bulk of LC that merged with the Saturn ring defect encircling the colloid. The silica colloid was trapped in the middle of the LC cell, and sank slightly downward. (D) SEM image of fiber-like structure that shows a bulk disclination line pinned to the bottom surface, as indicated by the bending white line. (E) SEM image of local LC director field inside an escaped region. Horizontally aligned fiber-like fractures indicating planar alignment of LC director field were found in the middle of the image, where the bending fiber-like fractures from top and bottom boundaries merged. (Scale bars: A, 20 µm; B–E, 3 µm.)