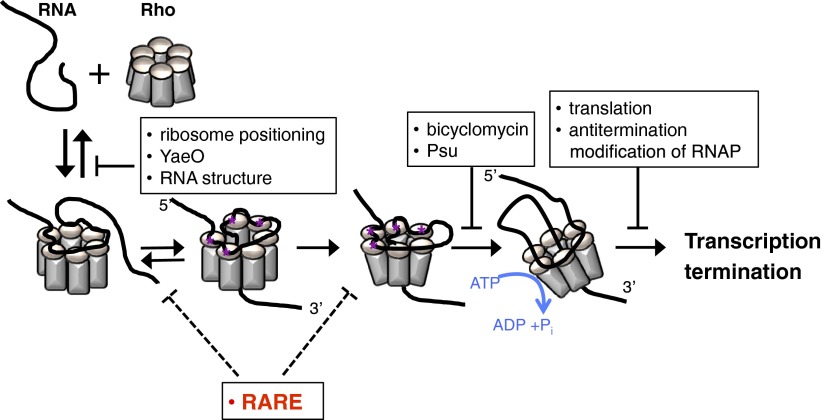
Fig. S5.
How RARE may inhibit Rho function. Schematic of proposed Rho recruitment pathway (9, 10), with modifications. A complex forms upon initial transient interaction between RNA (black) and a positively charged surface of the Rho hexamer (gray). Sequence-specific contacts (purple asterisks) between RNA and Rho primary binding site lead to ring opening and RNA threading through the central hole of the hexamer. RNA establishes contacts with Rho secondary binding site, leading to ring closure. Using the energy derived from ATP hydrolysis, Rho begins to translocate in 5′-to-3′ direction until it catches up with RNAP. RARE induces arrest of Rho recruitment process after the initial binding but before formation of the translocation-competent complex. The steps of the pathway targeted by other Rho inhibitors are shown for comparison purposes.