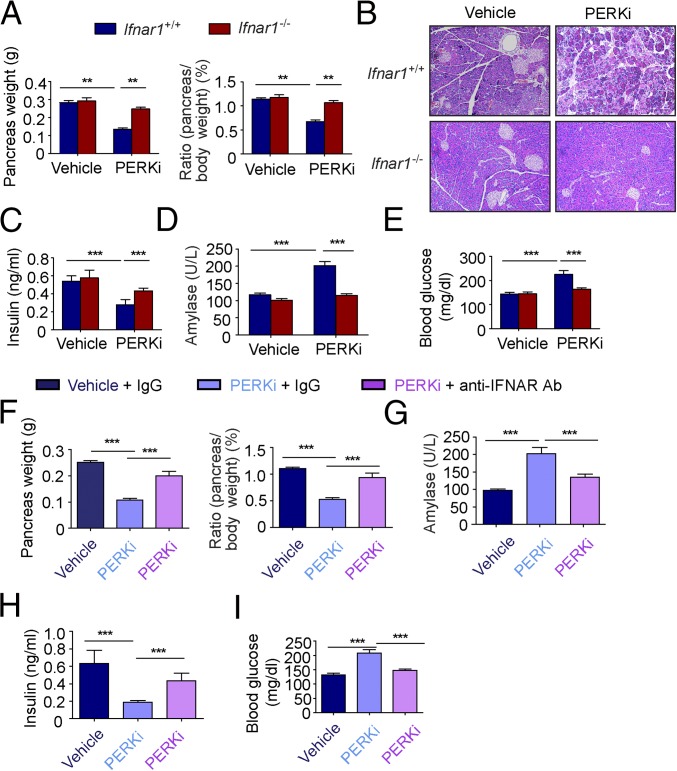
Fig. 4.
Pharmacologic inactivation of IFN signaling protects pancreas from toxic effects of PERK inhibitor. (A) Analysis of absolute (Left) and specific (Right) weight of the pancreatic glands from wild-type or Ifnar1−/− mice treated with vehicle or PERK inhibitor GSK2606414 (150 mg/kg) for 14 d. (B) Representative H&E staining of the pancreas from the mice treated as in A. (Scale bars, 100 µm.) (C) Analysis of serum insulin levels from the mice treated as in A. (D) Analysis of serum amylase levels from the mice treated as in A. (E) Analysis of blood glucose levels from the mice treated as in A. (F) Analysis of absolute (Left) and specific (Right) weight of the pancreatic glands from wild-type mice treated with vehicle or PERK inhibitor GSK2606414 for 14 d combined with anti-IFNAR1 antibody or its isotype control treatment (every 5 d, 1 mg i.p. injection per mouse). (G) Analysis of serum amylase levels from the mice treated as in F. (H) Analysis of serum insulin levels from the mice treated as in F. (I) Analysis of blood glucose levels from the mice treated as in F. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.