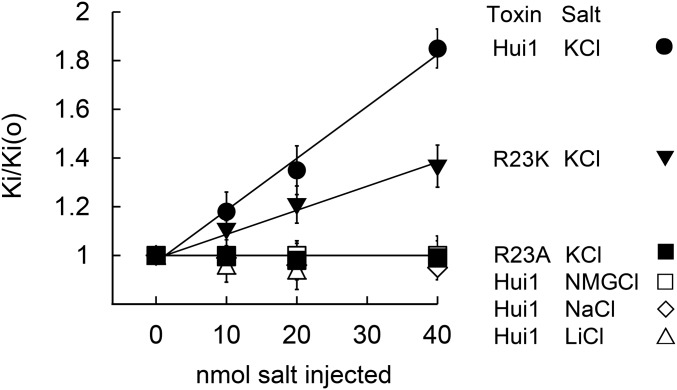
Fig. 4.
Hui1-Arg23 is responsible for voltage-dependent block. KcsA-Shaker was expressed in oocytes and studied by two-electrode voltage clamp to assess equilibrium inhibition and kinetic blocking parameters by the protocol in Fig. 3 at 0 mV after microinjection of 40 nL of 0.25 M to 1 M of the indicated salt (Tables 1 and 2). The change in Ki with voltage was due to changes in toxin dissociation rates. The dissociation rate of Hui1 was increased by microinjected KCl, but not by NMGCl, NaCl, or LiCl. The dissociation rate of Hui-Arg23Ala was insensitive to microinjected KCl or NMGCl, whereas the dissociation rate of Hui-Arg23Lys was less sensitive to microinjected KCl than wild-type Hui1. Oocyte solute space has been estimated to be ∼400 nL and intracellular potassium concentration to be ∼90 mM; therefore, a 20 nmol KCl microinjection should raise intracellular potassium by ∼50 mM to 140 mM, leading to an 11-mV shift in EK and a 50% increase in outward current (30, 31), close to the observed values here of 10 ± 2 mV and a 45 ± 9% (n = 4–6 oocytes). The new Ki were stable during the period of recording, that is, from 30 to 120 min after microinjection. Values are mean ± SEM.