Figure 4.
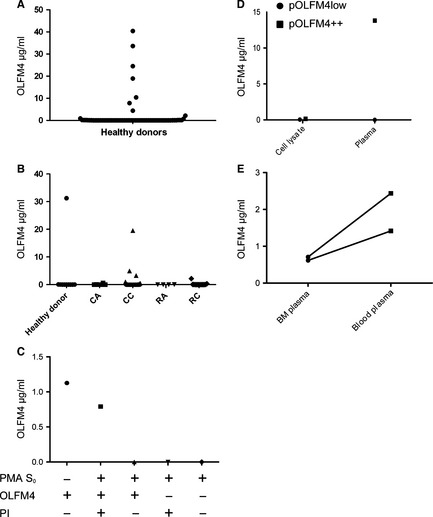
OLFM4 in plasma. (A) Plasma samples were obtained from healthy donors (N = 65) OLFM4 plasma concentration was measured by ELISA. (B) Plasma samples from patients offered first time ever colonoscopy. Depending on the endoscopy finding patients were divided into five groups: No neoplastic finding (N = 10), colon adenoma (CA) (N = 6), colon carcinoma (CC) (N = 23), rectal adenoma (RA) (N = 4) and rectal carcinoma (RC) (N = 16). OLFM4 plasma concentration was measured by ELISA. Baseline characteristics of patients are presented in Table S1. (C) Purified OLFM4 was added to either buffer or medium from neutrophils (108 cells/ml) stimulated to degranulate by stimulation with PMA 5 μg/ml (PMA S0) in the presence or absence of protease inhibitors (PI). OLFM4 concentration was measured by ELISA. (D) OLFM4 content in cell lysates (1 × 107 cells/ml) and plasma was measured by ELISA in an individual with low plasma OLFM4 (pOLFM4low) and in an individual with high plasma OLFM4 (pOLFM4++). (E) ELISA measurements of OLFM4 content in bone marrow (BM) plasma and blood plasma.
