Figure 6.
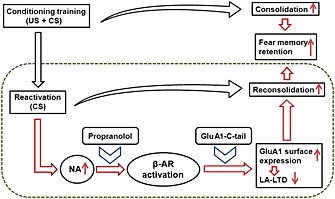
Scheme of the stages at which propranolol and GluA1‐C‐tail can interfere with fear reconsolidation. After acquisition of the associative fear memory (US + CS), drugs that strengthens the consolidation process lead to enhancement of fear retention. After fear reactivation (CS for one time), endogenous noadrenaline strengthens the process of reconsolidation, resulting in the enhancement of fear memory retention. Blocking β‐adrenoceptors by propranolol, or preventing the phosphorylation and surface expression of GluA1 subunitsby GluA1‐C‐tail overexpression in LA, attenuates reactivation‐induced fear memory retention. US, unconditioned stimulus (foot shock); CS, conditioned stimulus (tone).
