Figure 5.
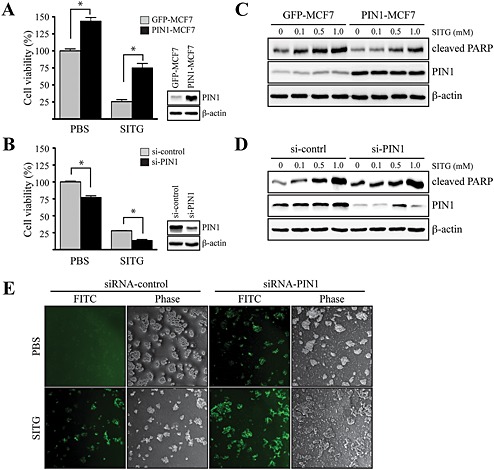
Inhibitory effects of sitagliptin on PIN1‐induced cell viability in MCF7 cells. (A) MCF7 cells, mock transfected (GFP‐MCF7) or overexpressing PIN1 (PIN1‐MCF7), were seeded and cultured for 24 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Then, the cells were treated with 1 mM sitagliptin (SITG) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay, as described in Methods. Data shown are the means ± SD, from triplicate experiments. * P<0.05, significantly different as indicated. (B) MCF7 cells were transfected with constructs expressing control (siRNA‐control) or PIN1‐specific (siRNA‐PIN1) siRNAs. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 1 mM sitagliptin for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay, as described in Methods. Data are represented as the mean ± SD, as determined from triplicate experiments. (C) GFP‐MCF7 or PIN1‐MCF7 cells were seeded and cultured for 24 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Then, the cells were serum starved for 24 h, exposed to the indicated concentration of sitagliptin for 48 h, harvested and lysed, and the lysate was immunoblotted. (D) siRNA‐control or siRNA‐PIN1 constructs were transfected into MCF7 cells. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were serum starved for 12 h, exposed to the indicated concentration of sitagliptin for 48 h, harvested and lysed, and the lysate was immunoblotted. (E) siRNA‐control or siRNA‐PIN1 constructs were transfected into MCF7 cells. After 30 h, the cells were serum starved for 12 h and then exposed or not exposed to 1 mM sitagliptin for 24 h, and DNA fragmentation induced by sitagliptin was measured.
