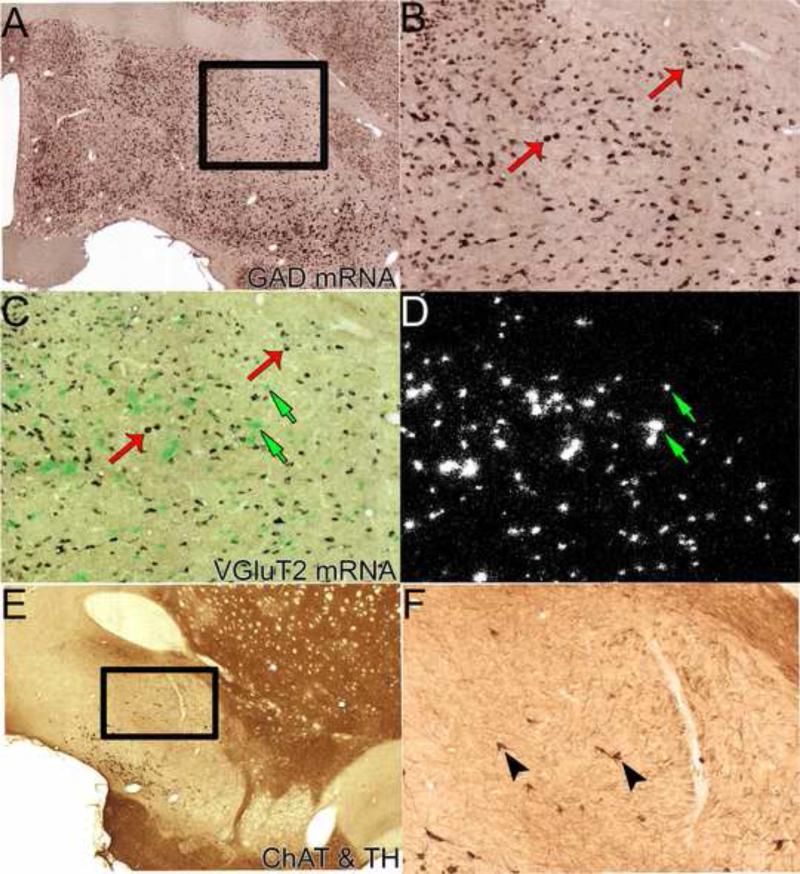
Figure 3. Neuronal phenotypes of the ventral pallidum.
A-B. GABAergic neurons. Double in situ hybridization; the purple labeled neurons display digoxigenin-labeling for GAD 65 and GAD 67 mRNAs. Box in A showing VP regions displayed in B, C, and D. B. Higher resolution photograph of GAD mRNA neurons. Note abundance of GABAergic neurons, two examples shown by red thin arrows. C-D. Glutamatergic neurons. The same section as B further processed with radioactive in situ hybridization for VGluT2 mRNA under brightfield (C) and darkfield (D) illumination. Clusters of green grains (C) or white grains (D) indicate VGluT2 mRNA neurons. Note abundance of glutamatergic neurons, uniquely localized within VPvm. Examples of VGluT2-expressing neurons indicated by green small arrows. E-F. Immunohistochemistry for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH; a marker for noradrenergic/dopaminergic elements) and choline acetyl transferase (ChAT; a marker for cholinergic elements). Boxed in region in the low power photomicrograph (E) is the region shown in the high power photomicrograph (F). The VP is delineated by fewer TH-fibers than neighboring structures (i.e., bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, interstitial nucleus of the anterior commissure, striatum, and tubercle). ChAT-labeled soma (brown diaminobenzadine reaction); two examples of cholinergic neurons are indicated by black arrow heads. Material from Dr. Root (Morales laboratory, NIDA).