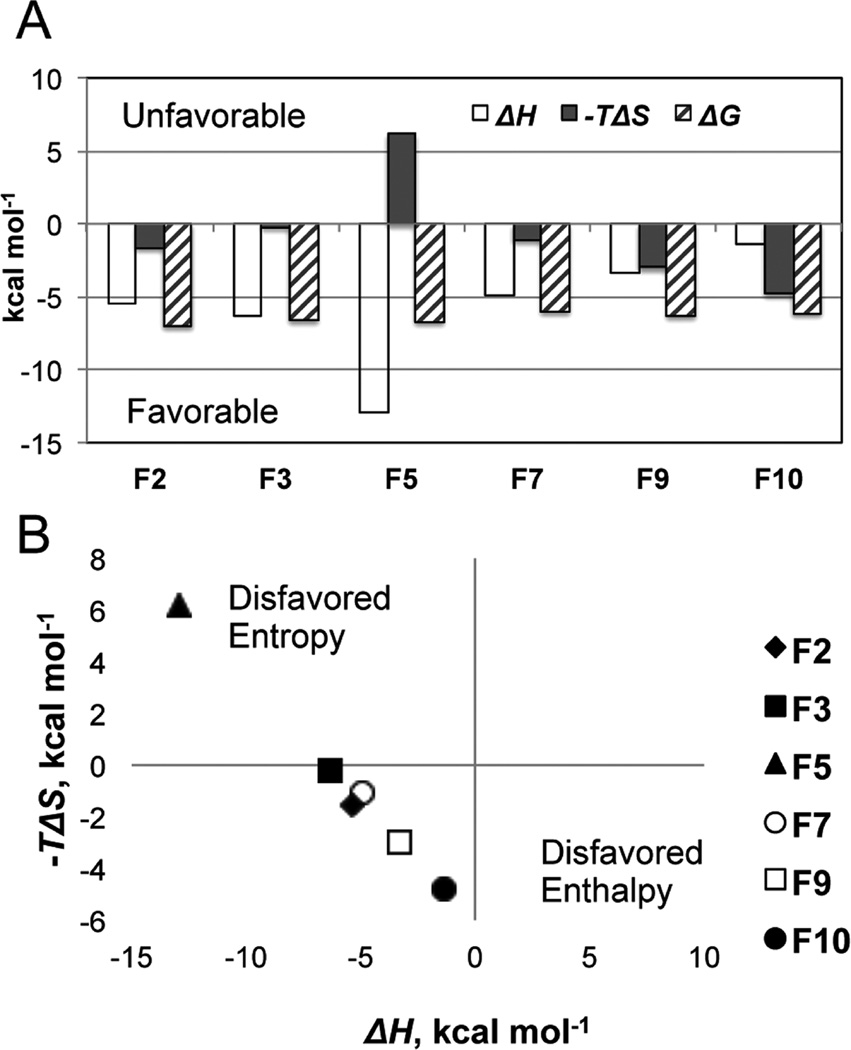
Figure 3.
Thermodynamic characterization of the fragment binding. (A) Histogram of the ΔH (open bars), −TΔS (filled bars), and ΔG (hatched bars). Negative values are favorable for binding. (B) Plot analyzing the enthalpic and entropic components of the binding energy and predictable enthalpy−entropy compensation. The binding of F5 is enthalpy driven; the binding of other fragments is enthalpy−entropy driven.