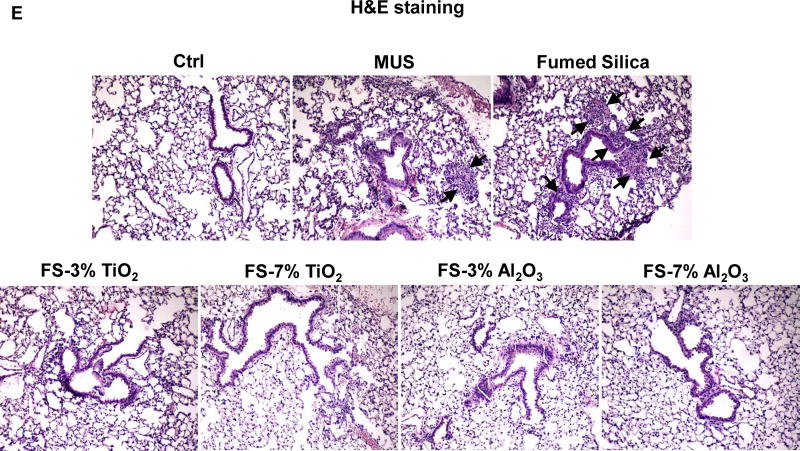
Figure 9. Ti and Al doping reduced pulmonary inflammation induced by fumed silica nanoparticles.
C57BL/6 (n=6) mice were exposed to 10 mg/kg of fumed silica by oropharyngeal aspiration. BAL fluid was collected to determine (A) neutrophil count, (B) IL-1β, (C) MIP-1α and (D) LIX levels at 6 h. MIN-U-SIL (MUS), a natural form of crystalline silica, was used as a positive control. *p<0.05 compared to control mice; #p<0.05 compared to fumed silica-treated mice. (E) H&E staining showed the presence of focal inflammation in the lungs, which was reduced by Ti and Al doping. The regions of focal inflammation are indicated by the arrows.