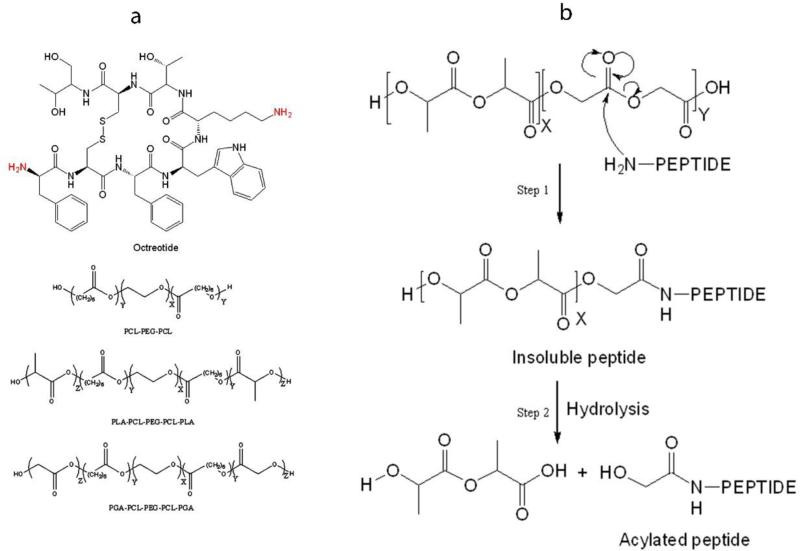
Figure 1.
(a) Structure of octreotide and polymers for MPs and gel. (b) Nucleophilic carbonyl-substitution mechanism of peptide acylation in PLGA microparticles. Nucleophilic attack of amine from peptide on partial positive carbon of degraded PLGA fragment results into formation of insoluble adduct (Step 1). Alcohol (-OH) and thiol (-SH) groups may also act as nucleophile (Murty et al., 2003). Hydrolysis of polymer side chain in insoluble peptide adduct results in release of soluble acylated peptide (Step 2).