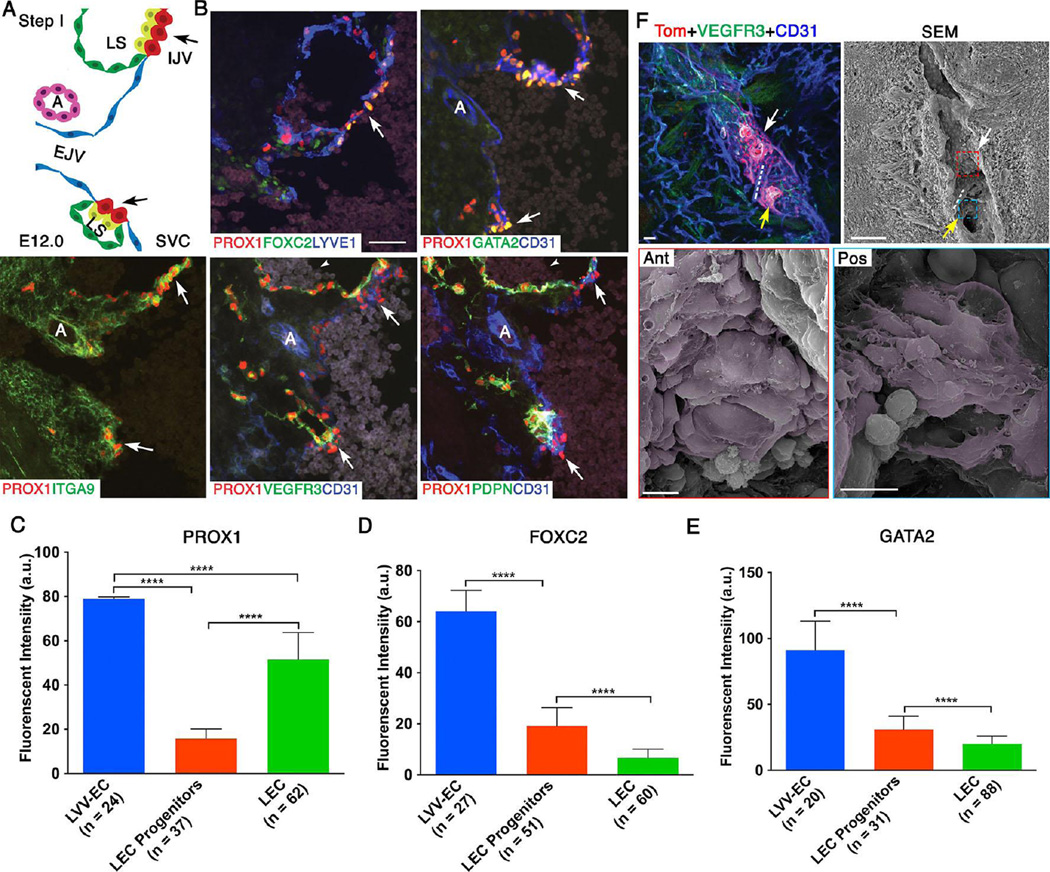
Figure 2. At E12.0 LVV-forming endothelial cells (LVV-ECs) delaminate from the veins in the luminal orientation.
(A) Organization of veins and lymph sacs (LS) in the frontal orientation at this first step of LVV development. Lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and LVV-ECs that form LVVs are in yellow and red respectively. The remaining LECs that form LS and venous endothelial cells are in green and blue respectively. EJV is perpendicular to IJV and SVC. (B) Immunohistochemistry for the indicated markers in the region from panel A. LVV-ECs are indicated by arrows. PROX1 is expressed at higher level in LVV-ECs compared to LECs. FOXC2 and GATA2 are expressed almost exclusively in LVV-ECs. In contrast, PDPN is restricted to LECs. VEGFR3 is higher in LVV forming LECs compared to LVV-ECs and the rest of LECs. ITGA9 is strongly expressed in the LVV forming LECs and LVV-ECs. Arrowheads point to the blood cells seen within the lymph sacs. (C-E) After performing immunohistochemistry on sections as described above, the fluorescent signals produced by antibodies were measured in arbitrary units (a.u.) using ImageJ software. PROX1 (C), FOXC2 (D) and GATA2 (E) are expressed at significantly higher levels in LVV-ECs compared to LEC progenitors and LECs. (F) 800 µm sagittal section of an E12.0 ProxTom embryo was immunostained and imaged by confocal microscopy. Two loose clusters of Tomhigh LVV-ECs are seen within the vein. Dotted line represents the artery located between the LVV-ECs clusters. SEM of the same section revealed delaminating LVV-ECs that overlap each other (pseudo colored in magenta) in both anterior (white arrow) and posterior (yellow arrow) clusters.
Statistics: n= 3 for B; n= 6 for F. For panels C-E, the indicated numbers of cells from a single embryo were analyzed. This data is representative of three-independent experiments. **** p<0.0001.
Abbreviations: LS, lymph sac; IJV, internal jugular vein; EJV, external jugular vein; SCV, subclavian vein; SVC, superior vena cava.
Scale bars: 50 µm for B and the top two panels of C; 10 µm for the bottom two panels of C.