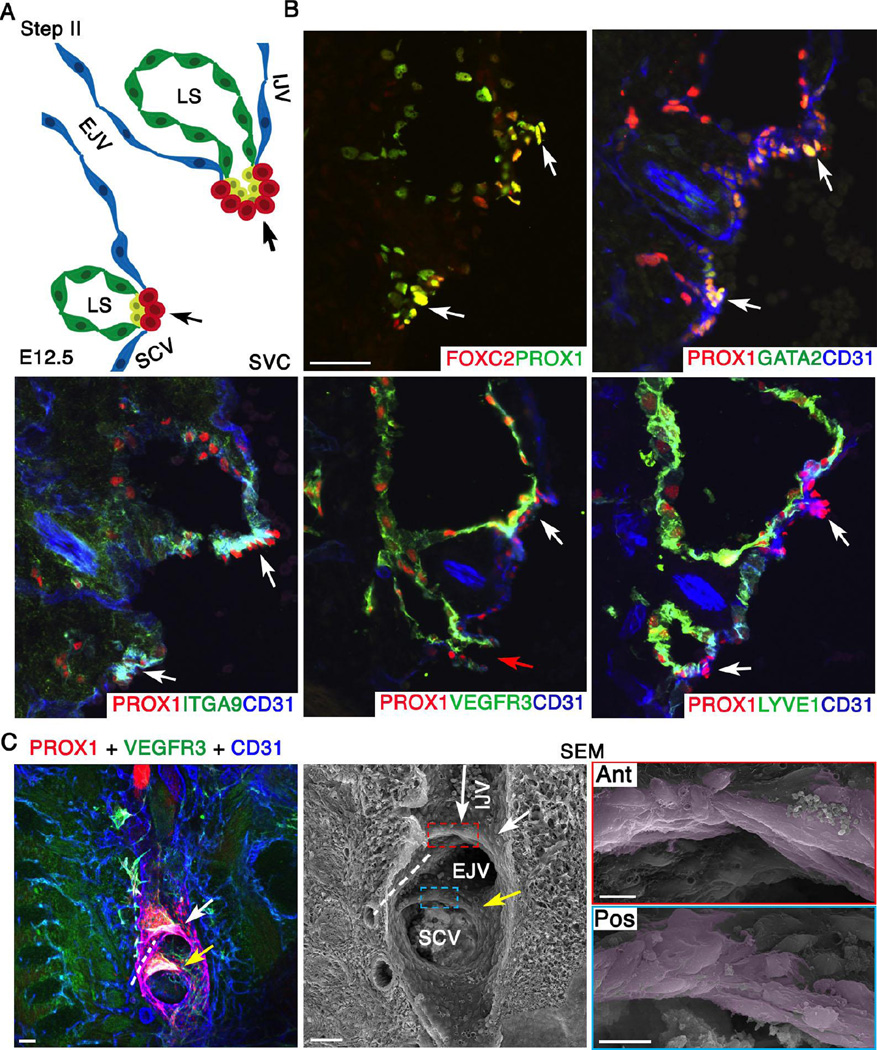
Figure 3. At E12.5 LVV-EC clusters invaginate into the veins and elongate perpendicular to blood flow.
(A) Schematic of the LVV complex in frontal orientation at E12.5. This is the second step of LVV development. Cells are color coded as in Figure 2. Note that the EJV has rotated clockwise towards IJV by 45°. (B) Immunohistochemistry revealed that the LVV-ECs (white arrows) have invaginated into the veins. And, a connection between LS and veins is seen (red arrow). LYVE1 is excluded from LVV-ECs at E12.5. Expression pattern of other markers is identical to that at E12.0. (C) Confocal imaging followed by SEM of an 800 µm sagittal section from a E12.5 ProxTom embryo revealed two compact Tomhigh LVV-EC clusters. Cells in both anterior (white arrow) and posterior (yellow arrow) clusters have elongated perpendicular to the direction of blood flow. The long arrow indicates the direction of flow in IJV. The flow from EJV and SCV are towards the reader. Dotted line indicates the artery between the two LVVs.
Statistics: n= 3 for B. n= 8 for C.
Abbreviations: LS, lymph sac; IJV, internal jugular vein; EJV, external jugular vein; SCV, subclavian vein; SVC, superior vena cava.
Scale bars: 50 µm for B and the first two panels of C; 10 µm for the last two panels of C.