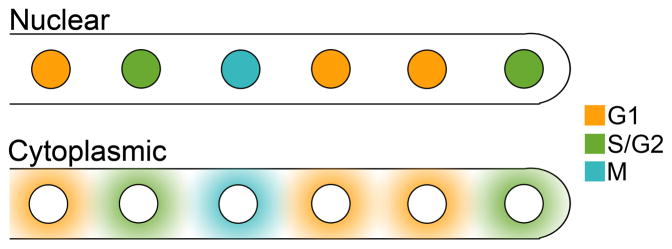
Figure 2.
Potential models for regulation of nuclear autonomy.
Top: Nuclear regulation of division autonomy. Nuclei carry with them the signals controlling their cell cycle stage. Nuclear movement and proximity to neighbors does not influence cell cycle stage.
Bottom: Cytoplasmic regulation of division autonomy. Regulators are spatially organized in the cytoplasm so that each nucleus is only exposed to the appropriate cell cycle signals. Bypassing and/or closely positioned nuclei may influence each others’ states.