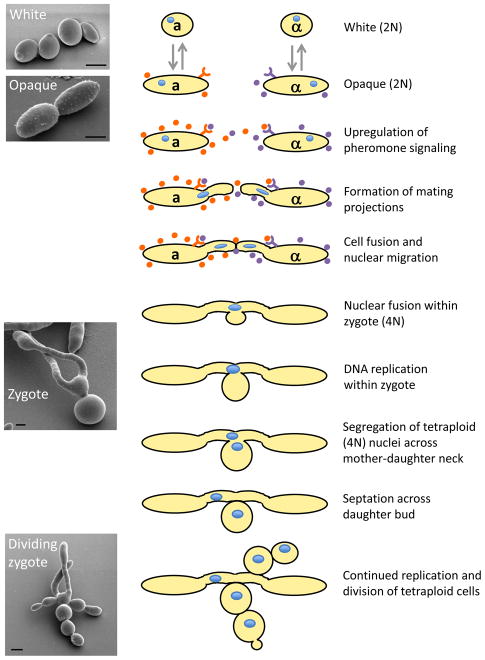
Figure 2. Mating in C. albicans.
Outline of the steps during heterothallic a-α mating in C. albicans. White cells switch to the mating-competent opaque form, and then undergo pheromone signaling between cells of opposite sexes. Mating projections fuse to form a mating zygote within which karyogamy (nuclear fusion) occurs. The nucleus in the tetraploid mating product undergoes replication, with one tetraploid nucleus entering the budding daughter cell. Continued replication and budding of tetraploid cells occurs. Scanning electron micrograph images of white, opaque and zygote cells are shown (scale bar, 2.5 μm, images courtesy of Matthew Hirakawa).